Stomach Diseases
Structure of stomach
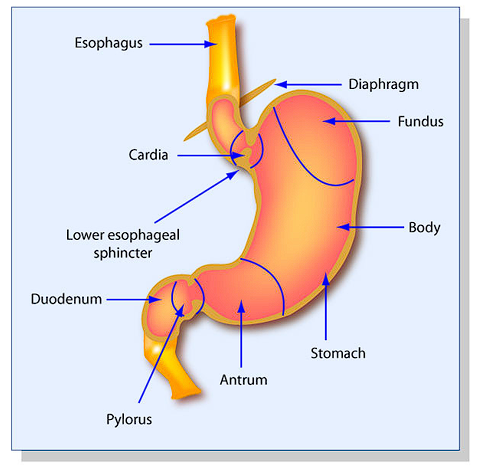
The stomach is a muscular, J-shaped organ in the top left part of the abdomen, linking the esophagus above and the small intestine below. Food passes in through the lower oesophageal sphincter, is churned and mixed with acid into a semi-solid state, and then passes through the pyloric sphincter into the duodenum for continued digestion and nutrient absorption.
Main Internal Parts of the Stomach
- Cardia
Where the stomach and esophagus meet.
Function: Swallowed food is received and has the lower esophageal sphincter to prevent acid reflux. - Fundus
Dome-shaped top, above the cardia.
Function: Storing food that has not been digested and traps gases produced by digestion. - Body (Corpus)
Middle, biggest portion.
Function: Primary location for mixing food with enzymes and stomach acid.
4. Lesser Curvature
Inner, shorter curve of the stomach.
Function: Route for food to travel along the inside rim.
5. Greater Curvature
Location: Outer, extended curve of the stomach.
Function: Offers attachment for ligaments and fat storage deposits (omentum).
6. Antrum (Pyloric Antrum)
Location: Lower region preceding the exit.
Function: Breaks up food into a paste (chyme) and controls passage to the pylorus.
7. Pylorus
Location: Narrow tube at the termination of the stomach.
Function: Passes chyme to the small intestine.
8. Pyloric Sphincter
Location: Where stomach meets duodenum.
Function: Controls amount and speed of chyme passed to the small intestine.
9. Rugae
Location: Folds within the lining of the stomach.
Function: Permit stretching of the stomach after meals and assist in churning food.
Pepsin
Pepsin is a stomach digestive enzyme that contributes to the digestion of proteins in food as smaller peptides. Pepsinogen is the inactive form produced, which activates after coming into contact with stomach acid. The highly acidic environment is where pepsin functions best and plays a critical role in efficient protein digestion.
5 major diseases of the stomach
- Gastritis
- GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
- Peptic Ulcer
- Stomach Cancer
- Functional Dyspepsia
1.Gastritis
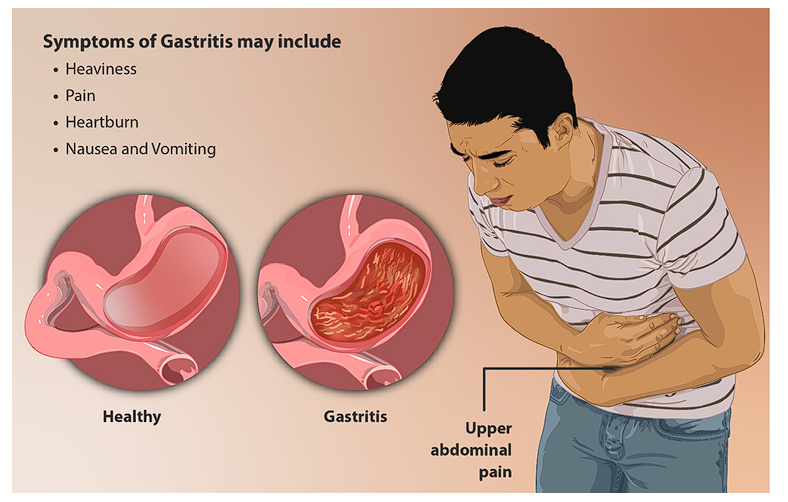
Gastritis is a condition where the lining of the stomach gets irritated or inflamed. It may develop abruptly (acute gastritis) or over time (chronic gastritis). Such underlying causes may be Helicobacter pylori infection, alcohol overuse, long-term use of drugs such as NSAIDs, stress.
symptoms
- Stomach pain – A burning, gnawing, or aching pain in the upper abdomen that may change with eating.
- Nausea and vomiting – Feeling sick and, in some cases, throwing up.
- Bloating – A feeling of heaviness or tightness in the stomach even after small meals.
- Indigestion – Trouble digesting food, often with discomfort after eating.
- Loss of appetite – Decreased desire to eat due to discomfort.
- Severe forms – Bleeding within the stomach lining, potentially leading to vomiting blood or passing black, tarry stools.
Causes
1.Helicobacter pylori infection: A type of bacteria that injures the lining of the stomach, leading to inflammation.
- Excessive alcohol consumption: Alcohol erodes and irritates the lining of the stomach, causing swelling and pain.
- Ongoing use of NSAIDs: Pain medicines such as aspirin thin the mucus in the stomach, leaving the lining open to acid injury.
- Stress: Extreme emotional or physical stress may increase acid in the stomach and cut off circulation, leading to inflammation.
- Foods and beverages: Spicy, acidic, or caffeinated foods and beverages can exacerbate irritation in some individuals.
Herbal Medicines for Gastritis
- Aloe Vera Juice – It Calms and inflames the lining of the stomach.
- Licorice Root (DGL form) – It Protects and heals the stomach by stimulating mucus production.
- Chamomile – Comforts the stomach and minimizes irritation through its anti- inflammatory effects. It is not commonly found in India.
- Amla (Indian Gooseberry) – Antioxidant-rich, supports digestion and heals the stomach lining. Don’t use amla much only use it if patient is very tired and sick.
- Shatavari – Soothes and heals the digestive system and stomach.
2.Peptic Ulcer
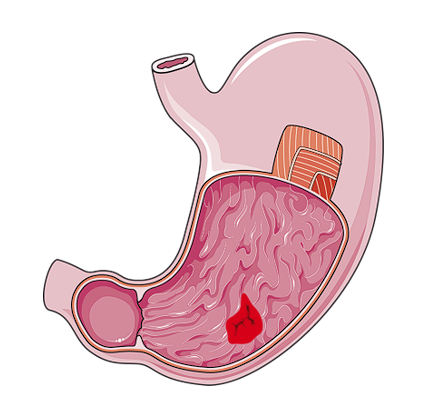
A Peptic Ulcer is an open wound or sore that occurs on the inside lining of the stomach, the beginning of the small intestine , or occasionally the esophagus. It occurs when the protective layer of mucus that covers these areas and protects them from stomach acid becomes weakened and the acid starts eroding the lining.
symptoms
- Burning stomach pain — The most frequent symptom. The pain typically occurs between the belly button and breastbone and can be made worse by an empty stomach.
- Bloating — Feeling bloated or full after meals.
- Heartburn — Burning in the chest due to acid reflux.
- Nausea or vomiting — Occasionally, the ulcer may lead to nausea or vomiting.
- Lossof weight and appetite — Because of pain or discomfort during eating.
- Fresh red blood in stool usually indicates bleeding in the lower parts of the digestive tract, such as the rectum or anus. Dark or black-colored stool (sometimes called melena) usually indicates bleeding higher up in the digestive tract, such as the stomach or small intestine.
Causes
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection
This bacterium weakes the stomach and duodenal lining, which is prone to acid damage and ulceration. - Diseases such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome result in overproduction of acid and enhance the risk of ulcers.
- Excess stomach acid production.
- Smoking decreases defensive factors in the stomach lining and slows recovery, raising the risk of bleeding.
- Stress and spicy foods
They won’t create ulcers themselves but will make symptoms worse and slow recovery.
Treatment for peptic ulcers
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs):
Medications such as omeprazole, esomeprazole, or pantoprazole decrease acid production to allow healing of ulcers. - H2-Receptor Blockers:
Medicines like ranitidine or famotidine also decrease acid production. - DGL Licorice (Deglycyrrhizinated Licorice)
Promotes mucus secretion in the stomach lining to guard against acid damage. Take in the form of chewable tablets or powder with meals to calm and heal ulcers without side effects of whole licorice. - Amla (Indian Gooseberry)
It is rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, and it encourages the repair of tissue and a reduction of inflammation.
It can be taken as fresh juice, powder, or capsules to enhance immunity and facilitate ulcer healing.
Slippery Elm Bark
It has mucilage content, which covers and calms the stomach lining and esophagus.
It is usually taken in the form of a warm tea or as a powder with water prior to meals.
Marshmallow Root
Another mucilaginous herb that creates a protective covering on the digestive tract.
Used as a tincture or tea to decrease inflammation and irritation.
Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory in nature.
Decreases inflammation and aids healing of ulcers.
Consumed in the form of a powder, juice, or capsule.
Precautions
- Avoid Painkillers (aspirin, ibuprofen, diclofenac).
- Long-term use of PPIs & H2-receptor blockers – not a permanent solution.
- Alcohol, smoking.
- Spicy, oily, fried foods.
3.GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
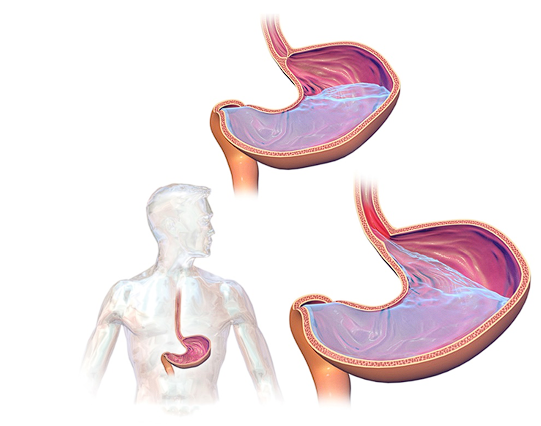
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) is a chronic digestive disease that causes stomach acid to regularly back up into the esophagus, leading to discomfort. This occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (the muscle between the stomach and the esophagus) weakens or relaxes too early.
Causes
- Weak or loose lower esophageal sphincter (LES): This gate between the stomach and esophagus does not close tight enough, allowing acid to flow back upward.
- Inadequate digestion and delayed emptying of the stomach: Food remains in the stomach for a longer time, growing acid content and risk of reflux.
- Consuming large meals or reclining within 90 minutes: Overstuffed stomach or reclining too early after meal forces acid into the esophagus.
Herbal Treatment for GERD
- Ajwain (carom seeds): Improves digestion, reduces bloating, and helps control acid reflux when taken after meals.
- Triphala: Aids gentle bowel movement, supports digestion, and helps prevent acid buildup.
- Fennel seeds: Cool the digestive tract, reduce acidity, and freshen the breath after meals.
- Ginger: Improves stomach emptying, reduces nausea, and soothes the digestive lining.
- Licorice (DGL form): Coats and protects the esophagus, reduces inflammation, and supports healing of the lining.
4.Stomach Cancer
Gastric cancer,or stomach cancer, occurs when abnormally growing cells occur in the stomach lining, usually as a result of H. pylori infection, poor nutrition, smoking, or family history. Symptoms are indigestion, stomach ache, bloating, weight loss, and occasionally blood in vomit or stool.
Herbal Medicine
- Turmeric – Contains curcumin, which possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant capabilities that can slow the growth of cancer cells and lower inflammation.
- Amla (Indian Gooseberry) – High in vitamin C and antioxidants, it promotes immunity, combats oxidative stress, and can potentially guard healthy cells from harm.
- Ashwagandha – An adaptogen that can lower stress, enhance immune response, and boost energy levels during cancer treatment.
- Unsweetened Green Tea – Has catechins (particularly EGCG) with antioxidant and anti-cancer activity that might slow the growth of tumors and shield cells.
5.Functional Dyspepsia
Functional dyspepsia is a very common condition of indigestion in which someone experiences persistent symptoms of indigestion—such as upper stomach discomfort, burning, bloating, or feeling full too quickly—without showing any disease or ulcer in the stomach or intestines on testing.
It’s usually associated with such causes as slow emptying of the stomach, hypersensitivity to stomach distension, stress, or foods.
Herbal Remedies for Functional dyspepsia
- Cardamom – Calms the stomach lining, lowers gas, and enhances digestion.
- Ginger – Triggers digestive juices, lowers nausea, and alleviates bloating.
- Cumin (Jeera) – Lowers acidity, enhances gut motility, and provides relief from gas.
- Coriander Seeds – Possess cooling and carminative action, lowering bloating and heartburn.
Lemon – Enhances digestive enzyme secretion and supports liver detox, but needs to be taken with caution when there is high acidity.

Naturopathic Tips
- To avoid stomach problems, eat warm cooked food don’t eat preservative food or food that is stored for long time of period.
- Avoid eating raw , spicy or fried food it can cause stomach problems.
- Eat small portion of meal , don’t overeat you can have frequent meals but don’t have it all in one go.
- Do yoga like vajrasana or pawan mukta for better digestion.
- Don’t directly go to bed after eating make sure to talk a little walk or sit.
Drink herbal tea for calming the stomach.

Conclusion
- Treat the root cause
- Triphala
Balances digestion, gently detoxifies the digestive tract, supports healthy gut flora, and helps with constipation and indigestion. - Licorice (DGL)
Heals and protects stomach lining and ulcers without side effects associated with normal licorice. - Marshmallow Root
Protects and calms the stomach lining, minimizing acidity and inflammation. - Ginger
Eases nausea, aids digestion, and decreases inflammation in the stomach. - Licorice (DGL)
Heals and protects stomach lining and ulcers without side effects associated with normal licorice. - Lemon Balm
Relieves indigestion, reduces bloating, calms stomach cramps, and has mild antispasmodic effects. - Cardamom
Stimulates digestion, reduces gas and bloating, and has carminative (anti-gas) properties. - Green Tea
Contains antioxidants that support gut health but take it in small quantity only 30 ml you can have it 3-4 times but in limited quantity. You can take it after food but not more than 30 ml. don’t boil the green tea.
- Combine Herbs , Diet and Lifestyle
- For healing and soothing, apply Aloe Vera, Licorice (DGL), and Slippery Elm to prevent inflammation and heal stomach lining.
- To ease digestion and gas, blend Ginger, Fennel Seeds, and Cardamom for efficient digestion and less bloating.
- For detoxification and regularity, consume Triphala, Amla, and Guduchi to detoxify the digestive tract and enhance immunity.
- To slow down inflammation and enhance immunity, blend Turmeric, Guduchi, and Chamomile.
- To soothe and anti-spasmodic effects, combine Lemon Balm, Chamomile, and Marshmallow Root to unwind stomach muscle and relief cramps.
- Support body with natural healing
Naturopathy trusts that the body has the natural ability to heal and stay in a state of balance if properly supported. It focuses on curing the cause instead of mere symptoms by re-establishing balance in the body naturally. Natural healing support includes the use of pure, plant-based medicine, wholesome nutrition, clean water, fresh air, and physical treatments such as hydrotherapy and massage. In addition to stress reduction and proper rest, these approaches activate the body’s own healing processes and enhance vital energy. By uniting lifestyle, diet, and natural remedies, naturopathy enables the body to eliminate toxins, heal tissues, and restore health in a sustainable and gentle manner—treating the body with respect and resilience.