HYPER ACIDITY AND STRESS
The Connection Between Hyper Acidity and Stress

The relationship between hyper acidity and stress highlights how mental strain can affect the body, especially in terms of digestive health.
Understanding Stress:
Stress impacts not only mental well-being but also physical health. The word “stress” originates from the Latin term stringere, meaning to “tighten” or “draw tight,” symbolizing the body’s response to pressure or tension. Stress can manifest both mentally and physically, affecting the mind, emotions, and body.
Stress occurs when external pressures or demands challenge the body’s ability to cope. It can be classified into two main types:
- Acute Stress: A short-term response to immediate situations, such as being caught in traffic or facing a tight deadline. This type of stress typically resolves once the situation passes.
- Chronic Stress: Long-term stress arises from persistent pressure, often linked to ongoing issues such as financial strain, heavy workloads, or emotional difficulties. Chronic stress can take a toll on physical health over time.
Understanding Stress: Types, Causes, and Solutions

Stress is an inevitable part of life that affects both mind and body. However, not all stress is the same, and it can be classified into different types based on duration and impact. In this article, we’ll explore the various forms of stress—acute, chronic, trauma, emotional, mental, and physical stress—along with their common causes and practical solutions for managing them.
Types of Stress:
1. Acute Stress and Chronic Stress:
- Acute Stress is short-term stress that arises in response to immediate perceived threats or challenges, like narrowly avoiding an accident or facing a tight work deadline. It tends to resolve quickly once the situation is under control.
- Chronic Stress, on the other hand, occurs when stressors persist over a long period. It might be due to ongoing issues such as a demanding job, financial struggles, or relationship problems. Chronic stress can have long-term health consequences, both mentally and physically, as the body remains in a heightened state of alert.
2. Trauma Stress:
Trauma stress occurs when an individual experiences or witnesses a traumatic event such as an accident, natural disaster, violent incident, or the death of a loved one. Trauma stress can lead to Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), characterized by flashbacks, nightmares, and heightened anxiety, making it difficult to cope with daily life.
3. Emotional Stress:
Emotional stress arises from personal situations that deeply affect one’s emotions, such as difficult relationships, significant life changes, or personal struggles. It can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, or sadness and can physically manifest as fatigue, insomnia, and poor dietary habits, as individuals may neglect their health during emotionally trying times.
4. Mental Stress:
Mental stress results from cognitive overload, often due to work pressure, academic challenges, or financial worries. This type of stress can lead to memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and decision-making challenges. Over time, unmanaged mental stress can harm both mental and physical health.
5. Physical Stress:
Physical stress directly impacts the body and can be caused by illnesses, injuries, or physical exhaustion due to overwork or strenuous activity. This type of stress can weaken the immune system, cause chronic pain, and slow down recovery from illnesses or injuries. Often, emotional or mental stress can exacerbate physical stress symptoms.
Common Causes of Stress:-
Stress can arise from various sources, depending on individual circumstances and personal coping mechanisms. Some common causes include:
- Work Pressure: High expectations, tight deadlines, or feeling overburdened.
- Overambition: Setting unrealistic goals can create excessive pressure.
- Lack of Sleep: Poor sleep patterns can increase vulnerability to stress.
- Health Issues: Chronic illnesses, digestive problems, or recurring health conditions.
- Family and Financial Struggles: Personal issues like family conflicts or financial instability.
- Death or Illness of a Loved One: Emotional toll from loss or hospitalization.
Managing Stress: Key Solutions:-
Effectively managing stress requires a blend of physical, emotional, and mental strategies. Here are some ways to manage different types of stress:
1. Relaxation Techniques:Practices such as deep breathing, yoga, and meditation can help calm both mind and body, reducing overall stress levels.
2. Time Management:Properly organizing tasks and setting achievable goals can help prevent cognitive overload and mental stress. Taking regular breaks and prioritizing tasks can improve focus and prevent burnout.
3. Emotional Support:Strong emotional connections with family, friends, or therapists can alleviate emotional and trauma stress. Talking openly about feelings and seeking support can provide relief and perspective.
4. Physical Care:Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate sleep can reduce physical stress and strengthen the body’s ability to manage other types of stress. A balanced lifestyle improves overall well-being and reduces the impact of stress on health.
5. Problem-Solving Skills:Breaking down problems and addressing them step by step can help reduce feelings of being overwhelmed, especially when dealing with chronic or mental stress.
6. Connection with Nature:Spending time in nature can refresh the mind and reduce stress. Activities like walking, gardening, or simply sitting outdoors can help improve mood and reduce stress levels.
While stress is unavoidable, understanding its different forms—acute, chronic, trauma, emotional, mental, and physical—can help us manage it more effectively. With the right strategies, such as relaxation techniques, time management, emotional support, and physical care, it is possible to reduce stress and lead a healthier, more balanced life.
Anti-Stress Hormones: Boosting Your Well-being Naturally

Our body is naturally equipped with its own powerful system to combat stress, known as anti-stress hormones. Unlike external medications such as antidepressants or stress-relief pills, the body can secrete these hormones through everyday activities, helping us manage stress effectively. Let’s dive into the main anti-stress hormones and explore how we can activate them naturally.
1. Endorphins: The Natural Painkiller:-
What are Endorphins?
Endorphins are natural chemicals produced by the body that act as neurotransmitters in the brain. They work both as hormones and neurotransmitters, playing a significant role in pain relief, mood regulation, and overall well-being.
Functions of Endorphins:
- Pain Relief: Known as the body’s natural painkillers, endorphins help reduce discomfort and promote relaxation.
- Mood Enhancement: Endorphins contribute to feelings of euphoria and happiness, often referred to as the “runner’s high.”
Activities to Boost Endorphins:
- Laughter Therapy
- Consuming Dark Chocolate
- Listening to Music
- Exercise
These simple activities trigger the release of endorphins, promoting relaxation and reducing stress naturally. However, engaging in unhealthy habits like alcohol and smoking can artificially stimulate these hormones, providing only short-term relief and exhausting the body’s ability to produce endorphins in the long run. It’s always better to stick to natural activities to maintain a healthy balance.
2. Oxytocin: The Love and Bonding Hormone:-
What is Oxytocin?
Oxytocin, often referred to as the “love hormone” or “bonding hormone,” is a neurotransmitter responsible for feelings of trust, emotional bonding, and affection. It plays a critical role in relationships and social connections.
Functions of Oxytocin:
- Emotional Bonding: Strengthens emotional connections between people, particularly family and friends.
- Social Interaction: Promotes feelings of trust, empathy, and closeness in social interactions.
Activities to Boost Oxytocin:
- Spending Time with Loved Ones
- Physical Touch (Hugs, Massage)
- Socializing
- Acts of Kindness
Oxytocin is naturally released during moments of trust and bonding, making it crucial for maintaining healthy relationships and emotional well-being.
3. Serotonin: The Mood Stabilizer:-
What is Serotonin?
Serotonin is both a neurotransmitter and a hormone, often referred to as the “happy hormone.” It plays a key role in regulating mood, sleep patterns, and appetite, while also promoting an overall sense of well-being.
Functions of Serotonin:
- Mood Regulation: Stabilizes mood and emotions, making us feel calm and content.
- Sleep and Appetite Control: Helps regulate sleep cycles and manage hunger.
- Feelings of Happiness: High serotonin levels are linked to increased feelings of happiness and well-being.
Activities to Boost Serotonin:
- Running
- Mindful Meditation
- Cycling
- Exposure to Sunlight
- Singing
These natural activities help increase serotonin levels, promoting a balanced mood and improving overall happiness.
4. Dopamine: The Motivation Booster:-
What is Dopamine?
Dopamine is often referred to as the “reward chemical” or “feel-good hormone.” It’s responsible for motivation, focus, and the feeling of accomplishment. Dopamine plays a significant role in boosting our energy and mood, especially in the morning.
Functions of Dopamine:
- Motivation and Reward: Drives us to accomplish tasks and feel rewarded afterward.
- Feelings of Pleasure: Regulates our sense of pleasure and achievement.
- Morning Energy Boost: Dopamine peaks in the morning, giving us the energy to start our day on a positive note.
Activities to Boost Dopamine:
- Exercise: Setting and achieving fitness goals releases dopamine, reinforcing positive behavior.
- Sufficient Sleep: Getting enough rest helps maintain dopamine levels.
- Enjoying Favorite Foods: Simple pleasures like eating your favorite meal or participating in a favorite hobby can trigger dopamine release.
Understanding Hyperacidity: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
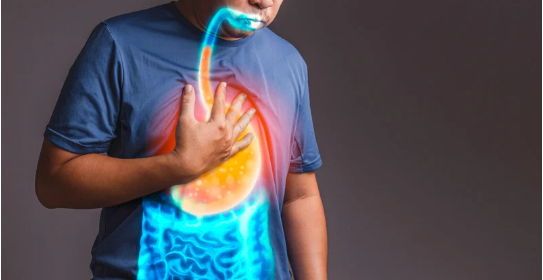
Hyperacidity, also known as hyperacidity or acid reflux, is a condition characterized by excessive production of stomach acid. This article explores the definition, symptoms, causes, and management strategies for hyperacidity.
What is Hyperacidity?
Hyperacidity occurs when there is an overproduction of stomach acid, which can lead to discomfort and irritation in the digestive tract. The primary component of stomach acid is hydrochloric acid (HCl), which plays a crucial role in the digestive process. While normal acid secretion is essential for breaking down food, excessive amounts can cause irritation and discomfort.
Key Points:
- Hyperacidity is often referred to as acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- It occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing symptoms like chest burning and irritation.
Symptoms of Hyperacidity:
Individuals suffering from hyperacidity may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Burning sensation in the chest (heartburn)
- Irritation in the throat or mouth
- Difficulty swallowing
- Nausea
- Bloating and gas
These symptoms can significantly affect daily life and overall well-being.
Causes of Hyperacidity:
- Diet:Spicy, fatty, and acidic foods can contribute to increased stomach acid production.Eating large meals or lying down soon after eating may exacerbate symptoms.
- Lifestyle Factors:Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are known contributors to hyperacidity.High levels of stress can also lead to increased acid production and worsen symptoms.
- Medications:Certain medications, particularly antibiotics, can disrupt the balance of stomach acid and lead to hyperacidity.It is common for doctors to prescribe additional medications to counteract this effect when antibiotics are needed.
- Medical Conditions:Conditions like GERD, peptic ulcers, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome can lead to hyperacidity.Emotional stress and anxiety can also trigger symptoms.
Management Strategies:
- Dietary Modifications:Avoiding known triggers such as spicy and fatty foods can help reduce symptoms.Smaller, more frequent meals may prevent excessive acid production.
- Lifestyle Changes:Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can significantly improve symptoms.Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and adequate sleep is essential for overall digestive health.
- Medical Treatment:Antacids and medications that reduce acid production may be prescribed by healthcare professionals.It is crucial to follow medical advice regarding the use of medications, especially after antibiotics.
Understanding Hyperacidity and Its Impact on Health

Hyperacidity can lead to a range of minor to major problems in the body. This condition occurs when there is an excess production of stomach acid, which can result in various health issues. Understanding the implications of hyperacidity is crucial for maintaining overall health.
Common Problems Associated with Hyperacidity:
Individuals experiencing hyperacidity may face several discomforts, including:
- Gas: Excess stomach acid can lead to increased gas production, causing bloating and discomfort.
- Acidity: This refers to a burning sensation in the stomach, often described as heartburn. It can be quite uncomfortable and may affect daily activities.
- Constipation: Hyperacidity can disrupt the digestive process, leading to constipation and irregular bowel movements.
- Gut Health Disturbances: The imbalance created by excessive acid can negatively impact gut health, leading to various gastrointestinal issues.
- Toxicity: Increased acidity can contribute to the buildup of toxins in the body, which can further complicate health.
- Elevated Uric Acid Levels: Hyperacidity may also lead to an increase in uric acid levels, which can result in conditions like gout and kidney stones.
The Connection Between Stress and Increased Stomach Acid Production

In our fast-paced lives, stress has become an inevitable part of daily existence. While stress is often linked to various health issues, its impact on the digestive system, particularly the production of stomach acid, is a significant concern. This article explores how stress influences stomach acid production, the physiological mechanisms involved, and potential solutions for managing stress-induced hyperacidity.
Understanding the Effects of Stress on the Body:
When individuals experience stress, several physiological responses occur, including the increased production of stomach acid. Stress stimulates the release of specific hormones and chemicals that can lead to heightened gastric acid secretion.
- Increased Stomach Acid Production:
Stress can prompt the body to release chemicals that increase stomach acid production. Excess stomach acid can overwhelm the esophagus and lead to acid reflux, exacerbating symptoms for individuals already suffering from hyperacidity. - Cortisol’s Role:
Cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone, plays a crucial role in muscle relaxation, including the smooth muscles involved in digestion. This relaxation can impact the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), creating an environment conducive to acid reflux. Consequently, individuals with pre-existing acid reflux conditions may experience aggravated symptoms during stressful periods.
How Stress Triggers Acid Production:
The relationship between stress and increased stomach acid production can be understood through the activation of the body’s stress response—commonly known as the “fight or flight” response. Here’s how it works:
- When a person experiences stress, the body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
- These hormones initiate a series of physiological changes to prepare the body for perceived threats or challenges.
- One of these changes is the stimulation of gastric acid secretion in the stomach.
- Additionally, the vagus nerve is activated, which leads to the release of gastrin—a hormone that regulates acid production.
- Prostaglandins, another group of compounds, can also be influenced by stress, impacting gastric function and contributing to hyperacidity.
Interconnectedness of Stress and Acidity:
It is essential to recognize that stress and hyperacidity are interlinked. Stress can lead to increased acid production, while hyperacidity can, in turn, cause stress, creating a vicious cycle. Understanding this connection is vital for effective management.
Solutions for Managing Stress-Induced Hyperacidity:
- Naturopathy Treatments:
Naturopathy offers various treatments to manage hyperacidity and stress. These include:- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs can help alleviate symptoms of hyperacidity and support overall digestive health.
- Yoga: Incorporating yoga into daily routines can significantly reduce stress levels and improve digestive function.
- Hydrotherapy: Utilizing water therapy techniques can aid in relaxation and alleviate symptoms of hyperacidity.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Stress Management: Identifying stress triggers and developing coping strategies can help reduce the overall stress response.
- Dietary Adjustments: Consuming a balanced diet that avoids trigger foods (e.g., spicy, fatty, or acidic foods) can help manage acidity levels.
- Cold Mud Application:
Research suggests that cold applications, such as mud packs, can provide a cooling effect on the body and help alleviate hyperacidity symptoms.
Understanding Yogic Management for Stress and Hyperacidity

In today’s fast-paced world, many individuals struggle with stress, anxiety, and related health issues, including hyperacidity. Yogic management offers a holistic approach to alleviate these problems through various practices, such as mindful meditation and relaxation techniques.
Mindful Meditation and Relaxation Techniques:
Among the various techniques, OmKara meditation is particularly effective. This form of meditation has been widely researched and is known to be beneficial for stress, depression, and anxiety. Regular practice can lead to significant improvements in mental well-being.
Surya Namaskar, a series of yoga poses, is another effective exercise that not only helps in loosening the body but also aids in stress management. Understanding the physiological changes that occur during yoga practice can help emphasize its importance.
Physiological Changes from Yoga:
Yoga leads to several physiological changes, such as relief from fatigue. It has been shown to alter cytokines and reduce inflammatory markers in the body. This evidence-based approach highlights the effectiveness of yoga in managing stress-related issues over time.
Some of the benefits of practicing yoga include:
- Weight Management: Yoga can help balance weight and improve body flexibility and strength.
- Physical Fitness: Regular practice enhances oxygen consumption and aerobic thresholds, leading to improved cardiovascular endurance.
- Deep Relaxation: Relaxation exercises and mindfulness meditation can help reduce somatization of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, ultimately improving metabolic and endocrine health.
Impact on Mental Health:
Yoga influences neurotransmitter levels, which can alleviate symptoms of depression. These benefits can be particularly pronounced when yoga is practiced consistently over extended periods.For individuals experiencing stress-induced hyperacidity, yoga can help address the root causes of their condition.
Hydrotherapy Treatments for Hyperacidity:
In addition to yoga, hydrotherapy treatments can be beneficial for managing hyperacidity. For instance, cold compresses applied to the abdomen can provide relief from acid reflux.
Other hydrotherapy treatments include:
- Cold Bath: Immersing the body in cold water.
- Cold Abdominal Pack: Applying cold packs to the abdomen for about 20 minutes.
- Alternate Abdominal Compress: Alternating between hot and cold applications, typically using three minutes of heat followed by one minute of cold.
- Kidney Pack: Applying cold over the stomach and hot over the back simultaneously for 20 minutes.
Other treatments include mud applications, which can be applied directly to the body or as a pack over the abdomen, and cold immersion baths.