ENDOCRINE SYSTEM AND DISEASES
Understanding the Endocrine System and Its Disorders
Welcome to the Saffron Educational and Medical Foundation. Today, we begin another opportunity to “be your own doctor” through the power of knowledge and self-understanding. This session is a repeat lecture that many students had requested through email and WhatsApp. The previous recording could not be uploaded due to technical issues, and several students were unable to attend. Considering the importance of this topic—especially with the increasing rise of hormonal disorders—we are conducting this lecture again.
Hormonal issues have become extremely common in today’s lifestyle. It is now observed that out of every five women, at least three face some form of hormonal imbalance. These problems may include irregular menstruation, PCOS, PCOD, amenorrhea, thyroid disorders, and several other endocrine-related conditions. Understanding the root cause of these issues is essential, because when we strengthen the foundation of the endocrine system, many other related problems automatically begin to resolve.
The endocrine system is a complex and intelligent network of glands and organs responsible for producing hormones. These hormones act as chemical messengers that regulate several vital functions, including growth, metabolism, reproduction, mood, digestion, and stress response. When this system works perfectly, the body produces only the required amount of hormones. However, when the endocrine glands malfunction, a wide range of disorders can occur.
Endocrine disorders can result from genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, tumor growth, injuries, or long-term stress. These conditions may affect the thyroid gland, adrenal gland, reproductive organs, or even the pancreas. The pancreas, though often associated only with digestion, is also a crucial endocrine organ because it secretes insulin—a hormone vital for regulating blood sugar levels. When insulin secretion becomes irregular, sugar levels fluctuate, leading to serious disorders like diabetes.
Our digestive system is another example of the body’s extraordinary intelligence. Normally, our body is accustomed to processing a certain amount of food each day. When we suddenly consume large quantities—such as during festivals or celebrations—our body may temporarily struggle. Symptoms like bloating, heaviness, or indigestion occur because the digestive system received more food than it is used to handling regularly. Fortunately, these issues are temporary. By giving the body rest the next day through fasting, liquid diets, or mild naturopathic cleansing, the system naturally resets and eliminates extra food load.
Similarly, the endocrine system is designed to produce a precise quantity of hormones each day. When everything functions smoothly, hormone levels remain stable. But due to internal disorders, stress, injury, or lifestyle disturbances, glands may begin producing hormones in excessive or insufficient amounts. Imagine a bowl that can hold only 100 ml of water. If we try to pour 200 ml into it, the water will overflow. The same happens in our body—when hormone production exceeds the required amount, it creates imbalances, leading to various diseases.
Understanding how the endocrine glands work and how hormonal disorders develop is the first step toward healing. Through naturopathy, many hormonal issues can be managed effectively by restoring balance, improving lifestyle, and supporting the body’s natural healing mechanisms.
The Importance of Hormonal Balance in the Endocrine System
Understanding Deficiency, Symptoms, Disorders, and the Role of the Pituitary Gland
The endocrine system maintains the body’s internal balance through the secretion of hormones. Just as excess hormone production leads to disorders, a reduction or deficiency in hormone secretion can be equally harmful. When the body produces too little of a required hormone, it fails to perform essential functions properly. This situation can be compared to hunger. When a person who is not habitual to fasting suddenly undergoes a complete fast for an entire day, they experience irritability, lack of focus, and constant thoughts of food. In the same way, when hormones drop below the required level, the body becomes unstable and begins to display disturbances that eventually manifest as disorders or diseases. Therefore, maintaining hormonal balance is extremely important to ensure overall health.
Hormonal imbalance—whether excess or deficiency—should never be ignored. Whenever there is a disturbance in secretion, it is almost certain that the body will respond through symptoms. These symptoms act as warning signs, giving us time to prevent further complications. Diagnosis can be made through careful observation, specific symptoms, and necessary blood tests. However, even before testing, individuals should develop the habit of listening to their bodies. The body often signals discomfort through fatigue, unusual cravings, irritability, changes in appetite, irregular sleep, or digestive disturbances.
Not every discomfort means disease. Sometimes the body is simply tired due to poor digestion, insufficient rest, or excessive workload. In such cases, the body may not respond normally for a short time. But when someone experiences repeated discomfort, abnormal symptoms, or persistent uneasiness, it becomes essential to reflect consciously on daily routines—What did I eat? Did I sleep well? Am I stressed? Am I overworked? This simple self-check allows early prevention, which is always better than cure. While it is true that illness cannot be avoided entirely—because life is unpredictable—awareness and timely action can protect the body from developing more serious endocrine disorders.
There are many endocrine disorders caused by hormonal imbalances in various glands. Some of the common conditions include acromegaly, adrenal fatigue, Addison’s disease, congenital adrenal hypoplasia, gigantism, thyroid disorders, diabetes, gestational diabetes, PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome), Cushing’s syndrome, Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, hypothyroidism, and Turner syndrome. All these conditions arise due to improper hormone secretion—either too much or too little. While some disorders like Cushing’s syndrome and Graves’ disease are relatively rare in Asian populations, others like PCOS, diabetes, and thyroid disorders have become extremely common and require greater attention.
Among the many endocrine problems, acromegaly is a significant but rare disorder that typically affects adults. It results from the overproduction of growth hormone. Growth hormone plays a crucial role in the development of the human body. Without it, the body would remain child-like, with incomplete physical and mental development. This hormone supports the growth of bones, muscles, organs, the brain, heart, and overall body structure. From birth until around 16 to 18 years of age, the human body grows rapidly, achieving maturity in height, weight, organ function, and cognitive abilities. Growth hormone makes this entire developmental process possible.
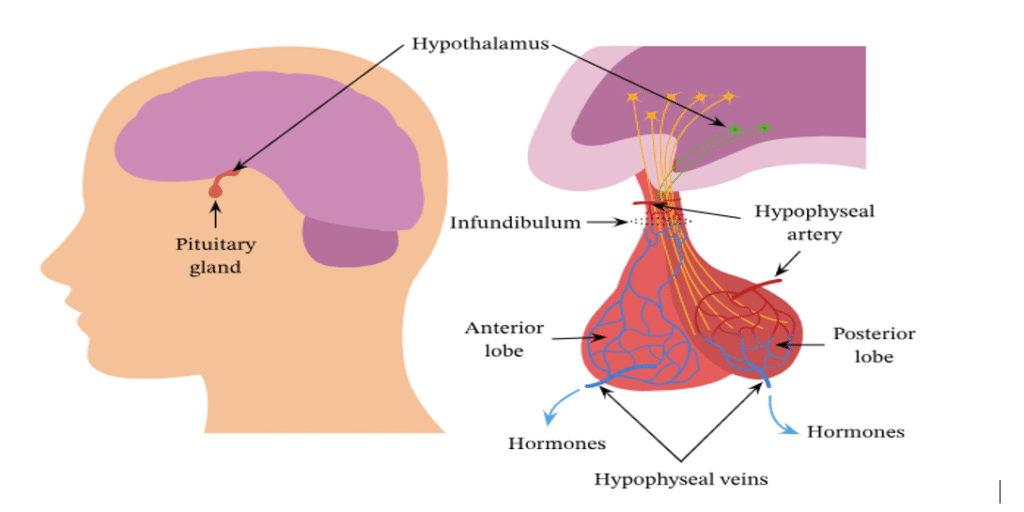
Acromegaly usually occurs when a small, benign tumor develops on the pituitary gland—often referred to as the “master gland.” The pituitary gland regulates and controls the hormonal activity of several other glands in the endocrine system. Because it plays such a central role, any imbalance within the pituitary gland can disrupt multiple hormonal functions throughout the body. Specifically, when the pituitary begins to overproduce growth hormone in adulthood, it leads to acromegaly, causing abnormal growth in certain body parts and multiple health complications.
Understanding the functioning of the pituitary gland is essential because it is the primary regulator of growth hormone secretion. Any disturbance in this gland affects not just growth but numerous bodily functions. As we proceed further, we will explore acromegaly in more detail, including its symptoms, diagnosis, and naturopathic approaches for management.
Acromegaly and Adrenal Fatigue: Understanding Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Acromegaly: When Growth Hormone Becomes Excessive
Acromegaly is a disorder caused by the excessive production of growth hormone in adults. Growth hormone is essential for the normal development of the human body, but when its secretion becomes uncontrolled, it leads to abnormal enlargement of different body parts. This hormonal imbalance affects physical appearance and disrupts normal functioning, making it a serious endocrine disorder that requires timely diagnosis and treatment.
The most common and early signs of acromegaly include noticeable changes in facial features. Individuals may develop enlarged lips, an unusually long tongue, and a broader or more pronounced jawline. The hands and feet often become significantly larger, which is one of the key indicators of the condition. These physical changes progress slowly, making it difficult for the person or family members to recognize the disorder in its early stages.
Acromegaly is usually caused by a benign (non-cancerous) tumor located on the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” controls the functioning of many other glands. When a tumor grows on the pituitary, it may force the gland to produce excessive growth hormone. Although it most commonly affects adults, a pituitary tumor can technically appear at any age, leading to abnormal height or body size depending on when the imbalance begins.
Extreme cases of acromegaly have even been recorded in global record books. For example, individuals with heights exceeding 11 feet have been documented. While such records may appear impressive, they reflect severe hormonal imbalance rather than a desirable physical trait. Many of these individuals face significant health challenges. Due to the excessive growth, the spine may bend, joints weaken, and mobility becomes difficult. People with severe acromegaly often require support such as a walking stick, even at a young age. Simple daily activities can become painful and exhausting. Thus, what appears extraordinary from the outside is often a painful struggle for the affected person.
Diagnosis of acromegaly involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and various tests. Depending on symptoms and their progression, doctors may recommend blood tests to measure growth hormone levels, as well as imaging tests like CT scans or MRI to identify pituitary tumors. The age at which symptoms start, the speed of growth, and the severity of physical changes all help in determining the degree of the disorder.
When it comes to treatment, modern medicine offers several options. Surgery is often the primary approach, especially when the tumor is causing excessive hormone secretion. Naturopathy and other alternative systems have their strengths, but they have limitations as well. For example, in cases where a person has an excessively long tongue that interferes with chewing, breathing, or swallowing, surgery becomes a necessary intervention. No amount of therapy or herbs can reduce the physical size of overgrown tissue once it reaches a critical stage. Therefore, surgical removal or reduction of the tumor is the most logical and effective approach in advanced cases.
Other available treatments include radiation therapy and specialized medications designed to control hormone levels. Science continues to evolve, offering new possibilities for better management of the condition. However, the first priority in any treatment plan is not cure but control—controlling excessive hormone levels to prevent further physical and internal damage.
Adrenal Fatigue: A Controversial Yet Common Condition
Adrenal fatigue is a term used by some practitioners to describe a collection of symptoms such as chronic tiredness, low energy, mood swings, poor concentration, and difficulty coping with daily stress. Although not formally recognized as a medical disease in conventional science, adrenal fatigue is widely acknowledged in alternative health systems, including naturopathy.
This condition is believed to arise from the overuse or exhaustion of the adrenal glands. These glands play an essential role in managing stress by producing hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. When a person faces prolonged mental, emotional, or physical stress, the adrenal glands may become overworked. This results in reduced efficiency, leaving the person feeling drained, fatigued, and unable to manage stressful situations.
In simple terms, adrenal fatigue is the body’s way of saying “enough.” Continuous stress—whether from work pressure, emotional strain, unhealthy lifestyle habits, or lack of rest—can eventually slow down the adrenal response. Although not considered a classical endocrine disorder, it is closely linked to overall hormonal health, because excessive stress disrupts multiple body systems.
The most important takeaway is that stress is not harmless. While short-term stress can be manageable, prolonged or excessive stress becomes harmful and contributes to hormonal imbalance. Whether recognized formally or not, the symptoms of adrenal fatigue are real, and individuals who experience them require proper rest, lifestyle correction, and supportive therapies to restore balance.
The Impact of Stress on Hormonal Imbalance and Understanding Adrenal Fatigue
Stress is one of the most powerful triggers of hormonal imbalance in the human body. While most people recognize that stress affects mood, sleep, and emotional well-being, very few understand the deeper and more serious impact it has on the endocrine system. When stress becomes excessive or long-lasting, it directly disrupts the secretion of hormones. Over time, this disruption can lead to chronic, sometimes irreversible, conditions that are difficult to treat. In such cases, individuals may have no option but to manage the condition throughout their life.
Stress does not only disturb the mind—it affects every organ and system. Constant mental tension interferes with sleep patterns, digestion, immunity, and internal chemical functioning. Hormones play a delicate role in maintaining balance, and even small disturbances can produce major changes. Therefore, when a person suffers from hormonal imbalance, it is essential to address stress first. Counseling becomes the primary step in healing, because a calm mind is necessary for the body to rebalance itself.
As practitioners, the first responsibility is to offer trust, confidence, and reassurance. These emotional supports often work better than any medicine. When a person begins to believe that recovery is possible, half of the disorder is already treated. The remaining part depends on therapy, dietary changes, herbal support, and lifestyle modification. But without psychological comfort, no treatment can show its full effect.
For conditions like adrenal fatigue—often associated with mental, emotional, and physical stress—it becomes even more important to understand the patient’s history thoroughly. Listening is a vital part of the healing process. Before prescribing remedies, a practitioner must identify the root cause: What kind of stress is the person facing? How long have the symptoms been present? What emotional burden are they carrying? This approach forms the basis of behavioral therapy, which is extremely helpful in supporting stress-related endocrine conditions.
Failing to diagnose properly can be risky. Many individuals with chronic hormonal issues experience anxiety, irritability, or severe mood swings. If left untreated, the stress can escalate to dangerous levels—some even develop suicidal tendencies due to prolonged suffering. Their hyper-reactive behavior can also unintentionally harm family members. Managing such cases requires sensitivity, patience, and correct therapeutic intervention.
The adrenal glands, located on top of each kidney, play a key role in managing the body’s stress response. When the glands are overburdened by continuous stress, they begin to function less effectively, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, irritability, and hormonal imbalance. One of the most noticeable symptoms of adrenal fatigue is the unusual craving for salt and sugar. A person may require salt three times more than normal for the same amount of food and still feel unsatisfied. Similarly, they may crave sugary foods constantly. Such cravings are the body’s way of signaling hormonal distress and reduced adrenal efficiency.
This symptom alone cannot diagnose adrenal fatigue, but it is a strong indicator—especially when combined with tiredness, mood fluctuations, sleep disturbances, and difficulty coping with stress. Identifying these signs early helps prevent further deterioration and allows the practitioner to guide the patient toward holistic recovery through rest, diet correction, counseling, and naturopathic support.
Understanding Addison’s Disease and Congenital Adrenal Hypoplasia (CAH)
Addison’s disease is a rare but serious endocrine disorder that occurs when the adrenal glands fail to produce sufficient amounts of two vital hormones—cortisol and aldosterone. These hormones play a central role in managing stress, regulating metabolism, balancing electrolytes, and maintaining blood pressure. When their production decreases significantly, the body begins to show multiple symptoms that gradually affect daily functioning.
One of the earliest signs of Addison’s disease is unexplained weight loss, often accompanied by severe muscle weakness and persistent low blood pressure. In some individuals, darkening of the skin may appear on both exposed and non-exposed areas of the body—a classic symptom known as “hyperpigmentation.” However, it is important to understand that not every dark spot or patch on the skin indicates Addison’s disease. Similarly, low blood pressure alone cannot be used to diagnose this condition, as many people naturally have a lower BP as a normal body tendency.
Proper diagnosis requires careful observation over time. Symptoms must be present consistently for several weeks or months. If the patient does not respond to regular treatment for common conditions such as thyroid imbalance, diabetes, or nutritional deficiencies, then the possibility of Addison’s disease becomes stronger. Only after evaluating the symptoms thoroughly and conducting appropriate laboratory tests—including hormone levels, electrolyte tests, and other adrenal function assessments—can a clear diagnosis be made.
The root cause of Addison’s disease is any factor that damages the adrenal glands. This damage may result from autoimmune disorders, severe infections, tumors, cancer, or conditions affecting the lymphatic system. Therefore, taking a detailed medical history is essential. If a patient has a known autoimmune disease, past or current infections, or a history of tumor or cancer, the chances of Addison’s disease increase significantly. Sometimes the disease develops because of these underlying conditions, and sometimes these conditions worsen because of the hormonal imbalance—it is a two-way relationship.
Modern medical treatment for Addison’s disease usually includes lifelong steroid replacement therapy, which substitutes the hormones that the body can no longer produce naturally. This helps the patient maintain normal bodily functions. From a naturopathic perspective, certain herbs and therapies can support adrenal health, improve energy levels, and help regulate hormonal balance. These natural methods are not replacements for emergency medical treatment but can complement modern medicine and improve overall well-being. At the end of the chapter, we will explore herbs and therapies that support the endocrine system holistically.
Congenital Adrenal Hypoplasia (CAH)
Congenital Adrenal Hypoplasia—often referred to as CAH—is an inherited group of disorders that affects the development and functioning of the adrenal glands. Unlike Addison’s disease, which typically appears later in life due to gland damage, CAH is present from birth and is caused by genetic mutations that impair hormone production.
In many individuals with CAH, the adrenal glands produce excess androgens (male hormones) while failing to produce adequate levels of cortisol and other essential hormones. This imbalance leads to a range of complications, depending on the severity and type of CAH. Since the adrenal glands play a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, stress response, and metabolic function, these hormonal disturbances can affect the child’s growth, development, and overall health.
Early detection is extremely important in CAH because untreated hormonal imbalance can lead to life-threatening conditions, especially in infants. Diagnosis is typically made through blood tests that measure hormone levels. Once identified, treatment involves long-term hormone replacement to correct deficiencies and regulate androgen production. Naturopathic therapies can be used in supportive care to improve immunity, metabolism, and adrenal resilience, but medical supervision is always essential.
Understanding Hormonal Imbalances: Addison’s Disease, Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH), and Gigantism
Hormonal health plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s overall balance. Although each hormone has its own specific function, no hormone works in isolation. The endocrine system works like an interconnected chain—if one hormone becomes imbalanced, it affects others as well. This article explains three important endocrine disorders: Addison’s Disease, Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH), and Gigantism, along with their symptoms, causes, and modern as well as naturopathic management approaches.
Addison’s Disease: When Adrenal Hormones Drop Below Normal
Addison’s disease is a rare endocrine disorder in which the adrenal glands fail to produce an adequate amount of cortisol and aldosterone. These hormones are responsible for stress response, blood pressure regulation, fluid balance, metabolism, and immune control. When their levels fall, the body begins to experience significant disturbances.
One of the most common symptoms of Addison’s disease is unexplained weight loss, accompanied by muscle weakness, fatigue, and low blood pressure. In many cases, patients also notice darkening of the skin, especially in both exposed and non-exposed areas. However, it is important to remember that dark patches on the skin do not automatically confirm Addison’s disease. Many people naturally have low blood pressure or experience weight loss due to thyroid imbalance, diabetes, chronic illness, or nutritional deficiencies. Therefore, diagnosis should always be made after observing symptoms for at least 15–20 days and confirming with specific medical tests.
Addison’s disease often arises due to factors that damage the adrenal glands. Autoimmune disorders are the most common cause, but infections, tumors, and cancers can also lead to adrenal destruction. A detailed medical history is essential, especially if the patient has suffered from autoimmune illnesses, long-standing infections, lymph node diseases, or any form of tumor or cancer. These underlying conditions may either cause Addison’s disease or develop as a consequence of it—both scenarios are possible.
Modern medical treatment primarily involves lifelong steroid replacement therapy, which helps restore the required hormonal levels. While modern medicine provides essential support, naturopathy can complement treatment through nutrition, herbs, and lifestyle modifications that support adrenal health and balance hormone production naturally.
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH): A Genetic Disorder Affecting Hormone Production
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, commonly known as CAH, is an inherited condition affecting the adrenal glands. In CAH, the body produces excess androgen (male sex hormone) but inadequate amounts of cortisol, and sometimes insufficient aldosterone. Because of this imbalance, several hormonal pathways become disturbed, leading to a variety of symptoms.
As discussed earlier, imbalance in one hormone often disrupts multiple others due to the interconnected nature of the endocrine system. In CAH, the excess production of androgens affects reproductive development and sexual organs, while low cortisol contributes to metabolic issues. Common symptoms include poor weight gain or weight loss, dehydration, vomiting, and nausea. One of the distinct symptoms is abnormal development of genital organs, especially visible in infants and children.
Because these symptoms differ significantly from other endocrine disorders, CAH can often be identified through careful clinical observation. If cortisol deficiency becomes severe, the patient may require synthetic cortisol to stabilize hormone levels. While natural foods and herbs can support cortisol production over time, emergency or severe cases require immediate medical intervention through hormonal replacement therapy. Nutrient-rich diets and adrenal-supportive foods can be introduced alongside medical treatment to improve long-term outcomes.
Gigantism: Excessive Growth Due to Growth Hormone Overproduction
Gigantism is a rare condition caused by excessive production of human growth hormone (HGH) during childhood or adolescence. The pituitary gland, located in the brain, is responsible for producing this hormone. When a benign pituitary tumor or genetic factor increases HGH secretion, the child experiences abnormally rapid growth.
The symptoms of gigantism are often easily visible. Children grow unusually tall and large compared to others their age. Physical features such as very large hands and feet, a protruding jaw, broader facial structure, and thick fingers and toes become noticeable. For example, a shoe size of 14–15 or more is common in individuals with gigantism, and many require custom-made footwear due to their unusually large feet.
Besides height, other changes include a prominent forehead, large nose and ears, and changes in facial proportions. The growth pattern can begin anytime from infancy to teenage years, depending on when the growth hormone imbalance begins. These visible symptoms differentiate gigantism from other endocrine disorders like CAH, where internal reproductive structures are primarily affected.
Gigantism shares similarities with acromegaly, another condition related to excessive growth hormone, but acromegaly occurs after the growth plates have fused in adulthood. Gigantism, however, occurs when growth plates are still open, leading to abnormal height and body growth.
Gigantism, Hyperthyroidism & Their Psychological Impact: A Detailed Understanding
Hormonal disorders not only affect the physical body but also deeply influence emotional and psychological well-being. Among the various endocrine disorders, Gigantism and Hyperthyroidism are conditions that present very visible symptoms, which often impact a person’s confidence and social life. The following article explains these conditions in detailed paragraphs, covering symptoms, causes, effects, and treatment options.
Gigantism: Visible Growth Changes and Their Cause

Gigantism is a rare hormonal disorder caused by excessive secretion of growth hormone (GH) from the pituitary gland. This hormonal overproduction begins in childhood—when the growth plates are still open—leading to abnormally rapid and excessive growth.
The physical signs of gigantism are usually very noticeable. Affected individuals may have unusually large hands, feet, fingers, toes, lips, nose, and ears. The jawline often becomes prominent, giving the face a different appearance. These changes occur because excess growth hormone affects every tissue and bone in the body.
The main cause behind gigantism is often a benign pituitary tumor, although genetic factors can also play a significant role. If a parent, sibling, or close family member has had similar hormonal issues, the next generation may be more prone to developing the disorder. However, even when it runs in families, it remains an extremely rare condition globally.
Modern treatments for gigantism include medications to reduce hormone levels, surgery to remove the pituitary tumor, or radiotherapy when required. Treatment choices depend on the severity of the condition. Not all patients need surgery; some can manage well with medications alone and live a relatively normal life.
Yet, when gigantism begins early in childhood and progresses rapidly, it can cause deep psychological and emotional challenges. Children may face teasing, bullying, or rejection from peers because society often finds it difficult to accept physical abnormalities. Many children with gigantism grow up feeling isolated, embarrassed, depressed, or mentally harassed. Schools may not always be equipped to support such children, leading to further trauma.
For this reason, psychological counseling becomes as important as medical treatment. Children must be taught that their differences do not define their worth. With emotional support, counseling, and family encouragement, they can build confidence and develop a strong mindset. In severe cases where growth becomes extreme and affects daily functioning, surgical or advanced medical therapies may be necessary.
Hyperthyroidism: When the Thyroid Becomes Overactive
Hyperthyroidism, also known as thyrotoxicosis, occurs when the thyroid gland produces more thyroid hormones than the body requires. The excess of thyroxine (T4) disturbs the body’s metabolism, causing multiple symptoms that affect daily life.
The thyroid gland plays a major role in regulating the body’s metabolic rate. Metabolism controls almost everything—weight management, digestion, growth, memory, stress response, immunity, and even sleep patterns. When metabolism becomes too fast due to excessive thyroid hormones, the entire body becomes imbalanced.
Hyperthyroidism is extremely common today. Out of every ten people, two or three may have thyroid-related issues like PCOS, hormonal imbalance, or unexplained weight changes. For many individuals who come for treatment of weight loss, menstrual issues, or hormonal imbalance, a history of thyroid dysfunction is frequently found.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include anxiety, nervousness, excessive sweating, fatigue, and sudden weight loss. The weight loss is often drastic and unexplained. Even if blood reports such as Vitamin B12, Vitamin D3, hemoglobin, and sugar levels are normal, the person may continue losing weight. If diabetes is ruled out and no nutritional deficiencies are present, then hyperthyroidism becomes one of the most common suspected causes.
The key difference between hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism is weight behavior:
- Hyperthyroidism → sudden, unexplained weight loss
- Hypothyroidism → weight gain, sluggishness, slow metabolism
To treat hyperthyroidism effectively, the first goal is to stabilize and balance the metabolic rate. When metabolism returns to normal, thyroid hormone levels also begin to balance naturally. Naturopathy supports thyroid health through diet, lifestyle correction, and herbal combinations, while modern medicine includes anti-thyroid medications, beta-blockers, or advanced therapies depending on severity.
Understanding Thyroid Disorders and PCOS: Causes, Diagnosis, Symptoms & Natural Management
Hormonal disorders are among the most common health concerns in today’s world, and two major conditions frequently seen—especially among women and young adults—are thyroid imbalance and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Both conditions affect hormonal secretion, metabolism, and overall health, often requiring medical attention and long-term lifestyle management.
This article explains these disorders in a simple, expanded, and detailed manner.
Thyroid Function Tests: The First Step in Diagnosis
Whenever a thyroid disorder is suspected, doctors recommend a series of tests such as T3, T4, TSH, and sometimes Free TSH or FSH (to check autoimmune involvement). These tests help identify whether the thyroid gland is producing too much hormone or too little.
- If test values fall in the normal range, the thyroid is functioning normally.
- If the values show imbalance, the condition may be either hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
Understanding these test results is crucial because they form the foundation for deciding the right treatment plan.
Causes of Thyroid Disorders: The Role of Iodine
One of the most common root causes of thyroid imbalance is iodine deficiency or excess iodine in the body. Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. When iodine levels are not adequate—either too high or too low—the thyroid gland struggles to function properly.
Fortunately, iodine is abundant in several foods, including:
- Rock salt, sea salt, and pink salt
- Green leafy vegetables
- Root vegetables like potatoes and sweet potatoes
Regular consumption of these foods helps maintain the body’s iodine balance, supporting healthy thyroid function.
Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. Because hormones become insufficient, the body’s metabolism slows down, leading to various symptoms.
Common Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
- Persistent tiredness and fatigue
- Weight gain, despite eating normally
- Bloating and puffiness
- Cold sensitivity — one of the most important and early signs
- Feeling giddy or low on energy
- Slowed metabolism
Compared to hyperthyroidism, where sudden weight loss occurs, hypothyroidism typically causes sluggishness, heaviness, and gradual weight gain.
Medical Treatment for Hypothyroidism
In modern medicine, hypothyroidism is treated with hormone replacement therapy, usually synthetic thyroxine (T4). Common medications include:
- Thyronorm
- Eltroxin
- Other levothyroxine formulations
Doctors determine the dosage based on:
- Age
- Gender
- Current hormone levels (TSH, T3, T4, FSH)
- Any associated health conditions
Most people begin with a low dose (often 25 mg) and increase gradually if required.
Reversibility Through Naturopathy
Unlike many other hormonal disorders, hypothyroidism is often highly reversible with proper naturopathic care. With the right combination of:
- Balanced diet
- Lifestyle correction
- Stress management
- Herbal therapy
- Detoxification practices
Many individuals experience major improvements within 6 to 8 months. Early detection is key. If addressed at the initial stage—whether during pregnancy, menopause, or teenage years—the thyroid imbalance can be corrected naturally without lifelong dependence on medication.
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
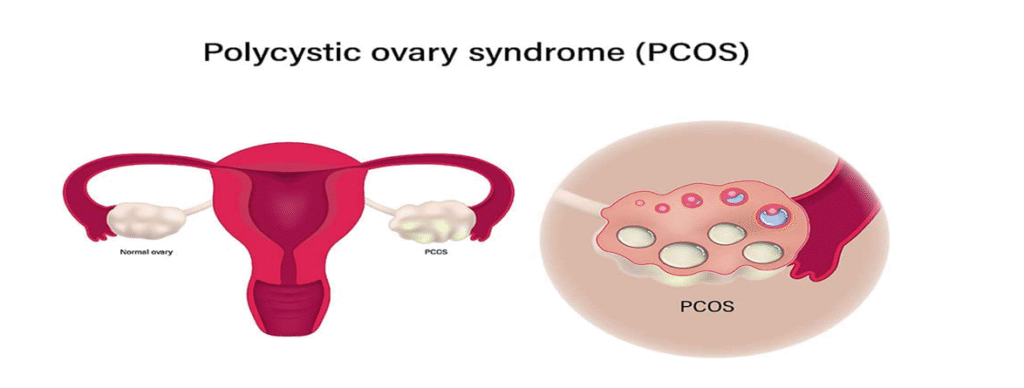
PCOS is a very common hormonal disorder that specifically affects the female reproductive system, particularly the ovaries. Women have two ovaries—left and right—responsible for egg formation and hormone regulation. PCOS interferes with this normal functioning.
Who Does PCOS Affect?
Today, PCOS has become extremely common, especially among:
- Teenage girls
- Women in their early 20s
- Women facing stress, poor lifestyle, or hormonal disturbances
It is caused by a combination of hormonal imbalance, insulin resistance, stress, and lifestyle patterns.
PCOS often coexists with thyroid disorders, making it important to diagnose both conditions simultaneously.
Hormonal Imbalances, PCOS & Diabetes: Understanding the Modern Lifestyle Crisis
Hormonal disorders—especially PCOS and diabetes—have become extremely common in today’s fast-paced world. Many women experience symptoms such as irregular periods, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), sudden acne flare-ups, and difficulty conceiving. Although these conditions have existed for decades, their prevalence has dramatically increased due to major shifts in lifestyle, stress levels, and daily habits.
PCOS: A Modern Lifestyle Disorder
One of the most concerning outcomes of uncontrolled PCOS is infertility, which is why we now see a rapid rise in IVF and IUI clinics. If PCOS is not managed in the early stages, it can gradually become chronic, making reversal extremely difficult. Restoring hormonal balance becomes a long and complex process once the condition progresses.
Symptoms and Hidden Signs
Besides irregular cycles and excessive hair growth, many women develop acne after the age of 25 or 30, even if they never had pimples in their teenage years. Such late-onset acne often indicates internal hormonal imbalance, frequently linked to PCOS.
Another contributing factor is the frequent use of contraceptive pills, often taken due to work schedules, lifestyle choices, or ritual-related reasons. Continuous hormonal pill intake can disturb the body’s natural cycle, further contributing to PCOS-like symptoms.
Why Is PCOS Increasing?
Although the exact cause of PCOS is still unknown, it largely involves:
- Genetics
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Lifestyle factors
However, nearly 90% of today’s cases are strongly lifestyle-related. Only a small percentage—around 10%—can be attributed to genetics. In earlier generations, PCOS was extremely rare. Women followed naturally healthy lifestyles, consumed wholesome food, and received adequate rest during menstruation.
Traditional Practices Had Scientific Reasons
In Indian culture, during the 3–4 days of menstruation, women were encouraged to rest, avoid heavy work, and reduce physical and mental strain. These practices were not superstitions—they were scientific measures to protect reproductive health. Adequate rest allowed:
- Hormonal balance
- Proper blood flow
- Reduced cramps and fatigue
- Healthier reproductive organs
As a result, earlier generations had fewer fertility issues and smoother pregnancies, often without the need for medical interventions like C-sections.
Modern Treatment Approaches
For managing PCOS, modern medicine generally relies on:
- Hormonal therapies
- Oral contraceptive pills
- Synthetic hormone supplements
These treatments help regulate cycles temporarily but require strict adherence to 21-day or monthly dosage routines. They manage symptoms but do not treat the root cause.
On the other hand, naturopathy, Ayurveda, and alternative therapies aim to reduce medication dependency. With disciplined lifestyle changes, many women can experience a gradual restoration of natural cycles, improved hormonal balance, and better long-term outcomes.
Lifestyle: The Key to Healing Hormonal Imbalances
Whether it is PCOS, thyroid issues, or diabetes, the foundation of healing lies in lifestyle modification. Important areas include:
- Proper rest and sleep
- Nutritious, balanced food
- Reduced screen time
- Stress management
- Moderate physical activity
Without correcting these basic habits, no medication or therapy can provide permanent results.
Diabetes: The Silent Killer
India is fast becoming the Diabetes Capital of the World. If as a society we do not change our habits, diabetes will affect future generations even more severely.
Diabetes occurs when the pancreas is unable to produce sufficient insulin, a hormone required not only for controlling blood sugar but also for regulating metabolism. Today, poor eating habits, sedentary lifestyles, chronic stress, and lack of awareness are leading causes of the rapid rise in diabetes cases.
Understanding Diabetes: A Growing Global Lifestyle Disorder
Diabetes is commonly known not only as a metabolic disorder but also as a liver-related disorder, because it affects the body’s entire metabolism and disrupts the normal functioning of several organs. In recent years, scientific journals across the world have published numerous studies highlighting how diabetes has become one of the most serious lifestyle diseases globally, affecting millions of people. Because of this rising concern, researchers are constantly exploring new ways to regulate insulin secretion from the pancreas and improve the activity of beta cells. This is important because insulin plays a crucial role—not only in maintaining blood sugar levels but also in supporting digestion.
Whatever food we consume must be broken down properly, absorbed effectively, and converted into nutrients that maintain our body’s strength and energy. Without insulin, this entire process cannot happen efficiently. When the body becomes resistant to insulin, several health problems begin to appear.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes
One of the earliest and most common symptoms of diabetes is excessive thirst, followed by frequent urination, far more than normal. In Type 1 diabetes, individuals often experience drastic and unexplained weight loss. In contrast, Type 2 diabetes patients may experience weight gain, especially because this type appears later in life—generally after puberty or during adulthood.
Alarmingly, today even very young children—sometimes as young as 4 or 5 years old—are being diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes. While genetics play a role, lifestyle factors and stress are major contributors. Research suggests that increasing academic pressure from an early age, long study hours, and reduced physical activity may be contributing factors to early-onset diabetes among children.
Different Types of Diabetes
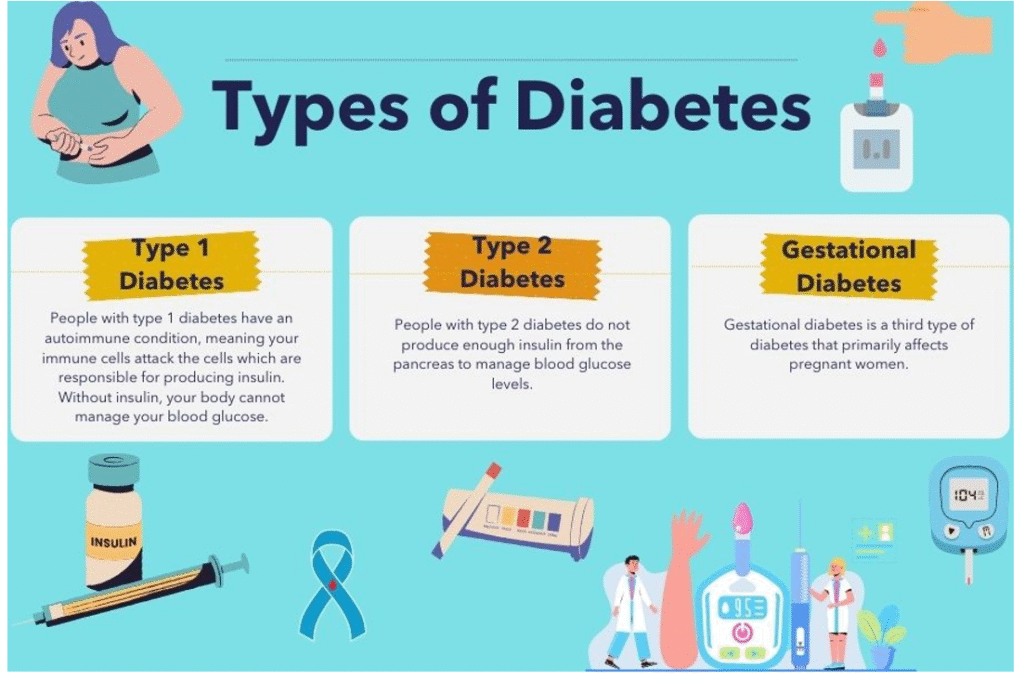
Diabetes can mainly be classified into:
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Onset is usually during childhood or puberty.
- The pancreas becomes almost inactive.
- Insulin secretion is nearly zero.
- Patients require lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- The most common form—over 92–93% of diabetic individuals fall under this category.
- Usually begins after adulthood.
- The pancreas still produces insulin, but not enough for the body’s needs.
- Strongly influenced by lifestyle and food habits.
- Gestational Diabetes
- Occurs during pregnancy.
- Needs careful monitoring to protect the mother and child.
To determine whether a patient has Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, endocrinologists or diabetologists use special tests such as C-peptide or other pancreatic function tests.
Is Type 2 Diabetes Reversible?
Yes—Type 2 diabetes is 100% reversible, provided the patient follows correct lifestyle measures. Certain levels of sugar are naturally required in the body. However, when levels drop too low, it leads to hypoglycemia, which can also be dangerous.
In conventional medicine, diabetes treatment includes lifelong medications, insulin injections, and in some severe cases, pancreatic surgery. The appropriate line of treatment always depends on the patient’s condition.
Role of Naturopathy in Managing Endocrine Disorders
Naturopathy strongly emphasises the role of food. Food is our primary source of energy—without it, we cannot survive. For diabetes, almost 80% of the improvement comes simply from correcting food habits. Based on 18–19 years of clinical experience, it is observed that when patients follow the right diet, lifestyle changes, and natural therapies, their HbA1c levels improve significantly, which is the most important indicator of long-term sugar control.
Instead of focusing on fasting and post-meal sugar values, naturopathy focuses more on bringing HbA1c to normal, which reflects healthy pancreatic function and stable insulin secretion.
Recommended Foods for Diabetes Management
Naturopathy recommends a diet rich in the following:
- Green and Non-Starchy Vegetables
Cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, radish, turnip, cucumbers, and leafy greens help maintain sugar levels and improve digestion.
- High-Fiber Foods
Fiber slows down sugar absorption, supports gut health, and prevents sudden sugar spikes.
- Healthy Fats
These include nuts, seeds, avocados, and cold-pressed oils that support metabolic health.
- Natural Spices
Spices like cinnamon, fenugreek, turmeric, and cumin help balance blood sugar naturally.
- Colourful Foods
Including a rainbow of fruits and vegetables ensures that the body receives antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals necessary for healing.
The Role of Balanced Foods, Fibers, Fruits, and Spices in Healing and Hormonal Balance
When it comes to healing the body and managing hormonal disorders, understanding which foods to include and which to avoid is extremely important. Many foods can support hormonal balance, while some may disrupt it if consumed in excess or during certain health conditions.
For example, in thyroid disorders—especially hypothyroidism—certain vegetables need to be avoided completely. In other endocrine imbalances, these foods may simply need to be balanced rather than eliminated. Cruciferous vegetables such as cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, radish, and turnips contain natural compounds that can either help or hinder hormone balance depending on how a patient’s body responds. Therefore, a personalised approach is always necessary. Being aware of this list allows practitioners to adjust a patient’s diet by cutting down or adding specific foods to improve their health condition.
Importance of Healthy Fats for Hormonal Balance
Healthy fats play a major role in maintaining hormonal balance and overall body function. Examples include nuts, seeds, cold-pressed coconut oil, peanut oil, and other natural oils. For non-vegetarians, eggs and lean meats are excellent sources of essential omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These good fats help the body form hormones, improve cell function, and support digestion of proteins. When the digestive system absorbs protein properly, the body’s hormonal system becomes more stable and balanced.
While occasional cheat meals are acceptable, your daily diet must include healthy fats from natural sources to support long-term wellness.
Why Fiber Is Essential for a Healthy Life
Fiber is one of the most essential components of a healthy diet. Without enough fiber, the body tends to develop constipation, and constipation is considered the root cause of many diseases in naturopathy. A healthy stomach leads to a healthy body, and fiber is the foundation of good digestive health.
Fibers support:
- Natural detoxification
- Liver function
- Gut microbiome balance
- Smooth bowel movements
Soluble fibers, found in oats, carrots, potatoes, sweet potatoes, legumes, and bananas, dissolve in water and help regulate blood sugar while supporting gut health. These foods are easily available and must be included daily—whether you want to stay healthy or recover from illness.
Insoluble fibers, found in beans, nuts, whole grains, and leafy greens, help add bulk to stool and prevent constipation. The key is to consume both types of fiber in the right proportions.
The Power of Colourful Fruits

Fruits are nature’s medicine, especially in Asian countries like India where each season brings a variety of nutritious options. Every 3–4 months, the seasonal shift provides us with new fruits rich in natural vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Now, as the Sharad Rutu ends and winter begins, fruits like strawberries, cherries, grapes, custard apple, guava (peru), papaya, mango, peach, plum, and pomegranate become available. These colourful fruits contain polyphenols and powerful antioxidants which reduce inflammation—the root cause of most hormonal disorders.
A single portion of fruit daily is strongly recommended.
The best time to consume fruits is in the morning for breakfast.
If you are undergoing treatment for hormonal imbalance, it is advised to avoid cooked breakfast and replace it with fresh fruits to reduce the digestive load and improve energy levels.
Healing Spices and Herbs for Everyday Wellness
Spices and herbs have been part of Indian cooking for centuries, not only for flavour but also for their medicinal value. They are naturally rich in anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and healing properties. Turmeric, for instance, is globally recognised today as a powerful medicinal spice.
Common healing spices include:
- Turmeric
- Black pepper
- Ginger
- Garlic
- Saffron
- Thyme
- Tulsi (Holy Basil)
These ingredients are already part of daily Indian meals—added to dal, sabzi, curries, and tadka. But when used for therapeutic purposes, their quantities need to be increased under guidance to maximise their healing potential.
Earlier, spices were used mainly to enhance flavour, but modern science and naturopathy recognise them as powerful tools for balancing hormones, reducing inflammation, and supporting overall health.
Holistic Lifestyle & Naturopathy Approach for Hormonal Balance
Maintaining hormonal balance is essential for overall health, and a disciplined lifestyle combined with the right naturopathy therapies can make a remarkable difference. If someone is already undergoing treatment, these natural practices can be added as supportive therapy. They work gently, without side effects, and help the body return to balance naturally.
Importance of Lifestyle Discipline
One of the biggest reasons for hormonal disturbances is an irregular routine. Discipline in sleep timing, food timing, work habits, and rest cycles plays a major role. It’s not just about eating homemade food—it’s about eating it at the right time every day. For example, having dinner at 7:30 PM one day and 10 PM the next day disrupts metabolism and digestion. Maintaining punctuality in daily habits improves digestion, boosts metabolism, and also reduces stress levels.
Role of Yoga & Exercise
Daily exercise helps maintain healthy hormone levels. Spending just 40 minutes a day on yoga, pranayama, and simple postures can show visible improvements within 10 days. These practices reduce stiffness, improve blood circulation, and help organs function optimally. Some of the most beneficial asanas include:
- Chakki Chalanasana – Good for abdominal strength
- Sabdandasana
- Malasana – Helps digestion and pelvic flexibility
- Butterfly Pose – Excellent for reproductive health
- Goddess Posture – Strengthens core and pelvic muscles
Even beginners who have never practiced yoga can start with these simple postures, easily available online or on social media for reference.
Magnet Therapy
Magnet therapy is also a supportive naturopathic technique. Rubbing a magnet (known as gou or gaue) on the soles of the feet for 5 minutes every night can help enhance energy flow and promote relaxation. This simple method supports hormonal balance and helps calm the nervous system.
Detox Therapy
Detox is a core principle of naturopathy, as a clean gut leads to a healthy body. Detox can be done in many ways:
- Fasting
- Liquid diet
- Use of detox herbs: Aloe vera, Amrita (Giloy), Haldi (turmeric)
Applying natural black sea mud on the abdomen for 20–30 minutes daily is particularly helpful, especially for females suffering from PCOS, PCOD, irregular periods, and other hormonal imbalances. The cooling and mineral-rich effect of mud helps regulate inflammation and supports reproductive health.
Hydrotherapy
Hot and cold water therapies are powerful tools in naturopathy. A 10-minute hot tub bath followed by a 10-minute cold tub bath improves blood circulation, reduces inflammation, and helps regulate the endocrine system. This contrast therapy relaxes the muscles and stimulates the hormonal organs.
Enema Therapy (Colon Cleansing)
Enema is one of the best ways to cleanse the digestive tract. Taking an enema for 3–5 consecutive days in a month helps detoxify the intestines, improves nutrient absorption, and enhances gut health. Since the gut and brain are deeply interconnected, improving gut health naturally helps in balancing hormones and improving mood, energy, and overall wellbeing.
Herbs for Hormonal Balance
There are several powerful herbs in naturopathy that act like natural medicines without side effects. These herbs are beneficial for all types of endocrine disorders and hormonal imbalances:
- Ashwagandha – Reduces stress, balances cortisol
- Shatavari – Supports female reproductive health
- Punarnava – Detoxifying and rejuvenating
- Tulsi & Tulsi Sudha – Enhances immunity and hormonal balance
- Wheatgrass – Rich in chlorophyll and essential nutrients
- Aloe Vera – Supports digestion and detox
- Amrita (Giloy) – Improves metabolism and immunity
- Ashokarishta – Useful for menstrual problems
- Triphala – Improves digestion and detoxifies the gut
- Rodra & Aipath – Beneficial for endocrine functioning
These herbs work gently and naturally, making them safe for long-term use under guidance.
Naturopathy Approach to Endocrine Health & Hormonal Balance
Maintaining endocrine balance is one of the most important aspects of overall health. Hormonal disturbances can affect metabolism, energy, growth, reproductive health, and emotional wellbeing. Naturopathy provides a safe, natural, and holistic approach to managing these imbalances through detoxification, herbal support, lifestyle correction, and yoga. When herbs and therapies are selected according to age, symptoms, and root causes, they work gently yet effectively to restore harmony in the body.
Understanding the Root Cause in Female Hormonal Disorders
Many female hormonal disorders—such as irregular menstrual cycles, menstrual cramps, menorrhagia, PCOS, infertility due to hormonal imbalance—are rooted in Pitta aggravation and poor digestive health. When Pitta increases, heat rises in the body, affecting the reproductive organs and disrupting normal hormonal rhythm.
- Detoxification: The First Step
Before introducing any herbs, detoxification is essential. Clearing the digestive system improves absorption, reduces inflammation, and balances the three doshas.
- Triphala is one of the best detox herbs. It gently cleanses the stomach, regulates bowel movements, and enhances overall digestion.
- Once the gut is cleansed, the body becomes more receptive to herbal treatments.
- Herbal Support for Female Reproductive Health
After detox, specific herbs can be introduced depending on symptoms:
- Kandarasa and Aipatikar help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce cramps, and relieve heavy bleeding.
- Ashokarishta is one of the most effective remedies for menstrual irregularities. It strengthens the uterus, balances hormones, and supports smooth monthly cycles.
- Rodra, when used along with aloe vera and Ashokarishta, is extremely beneficial for women experiencing hormonal infertility.
While structural issues such as blocked fallopian tubes may not respond to herbs, infertility caused by hormonal imbalance can be significantly improved with these combinations.
Herbs for Endocrine Disorders & Hormonal Regulation
Hormones related to growth, pituitary function, metabolism, and reproductive health can be naturally regulated through powerful herbs:
- Ashwagandha – Excellent for stress reduction, pituitary health, and improving growth hormone function.
- Shatavari – Supports female hormones, fertility, and reproductive wellness.
- Punarnava – Works effectively for inflammation and infections.
- Tulsi – A natural immune booster and hormone stabilizer.
- Wheatgrass – Considered the best superfood. It can be consumed fresh, powdered, or in tablet form. Saffron’s own organic wheatgrass is a highly beneficial and natural option.
- Aloe Vera – Supports digestion, detox, reproductive health, and hormonal balance.
- Amruta (Giloy, Tinospora cordifolia) – One of the most famous herbs in naturopathy. Giloy is a powerful body purifier and a tridosha balancer. When the three doshas are balanced, the entire hormonal system begins to function smoothly.
These herbs, when selected based on gender, symptoms, and associated health conditions, can be suggested to patients as part of a holistic healing plan. Combined with lifestyle improvements, they offer long-lasting benefits without side effects.
Role of Lifestyle & Exercise in Hormonal Balance
Herbs alone are not enough. Lifestyle correction is the foundation of hormonal healing. Patients must maintain disciplined routines for sleep, meals, work, and rest. Avoiding stress, eating at the same time daily, and avoiding junk or preserved foods greatly improves endocrine health.
Daily Exercise & Yoga

Regular movement is crucial. Yoga and pranayama, practiced for at least 40 minutes daily, help regulate hormones and improve blood circulation. Exercise enhances metabolism, controls weight, reduces stress, and optimizes endocrine gland function. Over time, patients experience better energy, reduced symptoms, and natural healing.
Guidance for Parents Concerned About Their Child’s Height
Many naturopathy practitioners receive queries from parents worried about their children’s height. Based on experience and observation, height improvement is possible up to 14–15 years of age when growth plates are still active.
Recommendations for Height Improvement
- Swimming and cycling are the two best exercises. Practiced at least three times a week, they effectively stimulate growth.
- Along with exercise, certain herbs can be added:
- Alfalfa
- Ashwagandha
- Wheatgrass
These herbs support growth, boost metabolism, and provide essential nutrients.
Food Habits to Avoid
Children should stay away from:
- Preserved and packaged foods
- Ready-to-eat snacks
- Sugary items like pastries, candies, and drinks
These foods interfere with digestion and metabolism, affecting natural growth.
Naturopathy Guidelines for Managing Endocrine Disorders, Diabetes & Patient Queries
Naturopathy offers holistic solutions for managing hormonal disorders, metabolic diseases, and chronic conditions without causing side effects. During clinical practice, practitioners encounter various questions regarding herbs, lifestyle changes, patient management, and the limitations of naturopathy. The following article presents a detailed, expanded explanation of these common queries, helping students and practitioners gain clarity and confidence.
Herbal Support for Hormonal Balance
While discussing endocrine disorders, one of the most common questions is about the exact herbs to prescribe. Three primary herbs that work wonderfully for metabolic and hormonal health include:
- Alfalfa
- Wheatgrass
- Ashwagandha root powder
These herbs may be provided in powder or tablet form, depending on the patient’s convenience. A standard prescription involves consuming them twice a day, preferably with warm water or as directed based on their constitution.
Along with herbs, basic diagnostic tests such as CBC with ESR are essential. A Complete Blood Count provides foundational insight into inflammation, infection, nutritional status, and overall metabolic health. ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate) further helps detect hidden inflammation—useful in endocrine and autoimmune cases.
Queries Related to Diabetes Management
- Type 1 Diabetes: What Can Naturopathy Do?
A common query is whether Type 1 diabetes can be reversed through naturopathy. Based on experience and clinical observation, Type 1 diabetes cannot be reversed, because it is an autoimmune condition where the pancreas permanently loses its insulin-producing capacity. These patients rely on insulin injections throughout life.
However, naturopathy can help Type 1 diabetic patients in the following ways:
- Minimizing insulin dosage with better diet and lifestyle
- Stopping other oral medications if unnecessary
- Improving digestion, metabolism, and stress levels
- Enhancing overall quality of life
The aim is not reversal but supportive improvement.
- Type 1 Diabetes and Seizures
Another concern practitioners face is whether Type 1 diabetes can cause seizures. While seizures are not common, they can occur due to:
- Family history
- Significant blood sugar fluctuations
- Emotional distress linked to lifelong insulin dependency
- Irritation or psychological stress due to frequent injections
It is important to clarify that Type 1 diabetes does not automatically lead to seizures, but emotional and neurological imbalances may trigger them in certain individuals.
Understanding Reverse Effects of Herbs
Sometimes patients report that a herb does not suit them. This is not a side effect—rather, it is a reverse effect, meaning the herb does not match their current internal condition. For example, someone with already aggravated internal heat may not tolerate certain heating herbs like coriander seeds in concentrated amounts. Individual constitution must always be considered before prescribing.
Lifestyle Diseases: The Link Between Diabetes, Thyroid & Cholesterol
Many practitioners observe that conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, and high cholesterol often appear together. These are interconnected lifestyle disorders and can be managed effectively through holistic living.
Before starting thyroid treatment, naturopathy recommends correcting:
- Food habits
- Rest and sleep patterns
- Daily routines
- Exercise and yoga practice
Once diabetes and high blood pressure are brought under control through lifestyle improvements, it becomes much easier to regulate thyroid function as well. This reduces the need for medication and improves the functioning of endocrine glands.
Lifestyle as the Foundation of Treatment
Whether the patient is dealing with fatty liver, diabetes, hormonal imbalance, or thyroid issues, the core solution remains the same:
- Regular exercise
- Consistent food timings
- Avoiding processed foods
- Adequate sleep
- Stress control
- Detoxification therapies
- Inclusion of herbs based on symptoms
When patients follow these guidelines consistently, they see major improvements—not only in specific disorders but in overall wellbeing.
Naturopathy Insights: Lifestyle, Diabetes, and Holistic Health Management
Managing chronic lifestyle diseases such as diabetes, fatty liver, and high blood pressure requires a holistic approach that focuses on lifestyle modification, diet, natural remedies, and gradual improvement. Naturopathy emphasizes that controlling the root cause—namely lifestyle factors—leads to significant improvements in metabolic and endocrine health over time.
- Lifestyle Changes: The First Step
The foundation of naturopathic treatment for chronic diseases begins with lifestyle changes. Many conditions, including fatty liver, diabetes, and high blood pressure, are often the result of long-term unhealthy habits such as irregular meals, processed food consumption, stress, and sedentary behavior. By implementing simple, yet consistent changes in daily routines, exercise, food habits, and sleep, patients can experience gradual improvement in their health.
For example, women with fatty liver have shown visible improvement over time when they follow a disciplined lifestyle and consume nutrient-rich, anti-inflammatory foods. Controlling lifestyle-related factors not only helps reduce inflammation and liver fat accumulation but also strengthens overall metabolic function.
- Role of Diet and Herbal Remedies
Diet plays a crucial role in managing lifestyle diseases. Good food choices not only support liver function and metabolic health but also reduce systemic inflammation. Herbs and natural remedies can be incorporated as supplements or adjunct therapy to enhance results.
For diabetic patients, herbs such as alfalfa, wheatgrass, and ashwagandha have been effectively used in powder or tablet form to help stabilize blood sugar levels. These remedies are considered natural medicines and are often processed in scientifically standardized ways (like drying) to ensure consistency and potency.
- Diabetes Management with Naturopathy
A common misconception is that naturopathy can completely reverse diabetes. In reality, the goal is not immediate reversal, but rather gradual control of sugar levels, reduced reliance on medication, and improved quality of life.
- For patients taking insulin, a naturopathic approach may help gradually reduce insulin dosage, under medical supervision.
- Continuous monitoring of blood sugar levels—such as fasting glucose and postprandial sugar—is necessary to safely adjust diet, herbs, and exercise.
- Lifestyle interventions, including proper sleep, stress management, and regular exercise, complement herbal therapy and improve metabolic outcomes.
- Managing High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is another lifestyle-related condition commonly seen alongside diabetes. Naturopathy focuses on dietary moderation, adequate hydration, stress reduction, and exercise to control blood pressure naturally. Maintaining a minimum of 2,000 ml of water per day is often recommended to support kidney function and circulation. Regular physical activity and herbal supplements further aid in stabilizing blood pressure levels.
- Patient Guidance and Education
A critical aspect of naturopathy is patient education. Practitioners guide patients on how to gradually reduce dependency on medications while managing their condition through lifestyle, diet, and natural remedies. Encouraging patients to understand the mechanism behind their illness, emphasizing realistic goals, and explaining the role of herbs and diet can significantly improve compliance and outcomes.
For example, patients and their families often ask about herbal remedies for diabetes. Explaining that herbs like alfalfa, wheatgrass, and ashwagandha act as natural stabilizers and metabolic supporters helps them feel confident about integrating naturopathic care alongside conventional medicine.
- Support Beyond the Clinic
Even after consultation, naturopathy emphasizes continuous support. Students and practitioners are encouraged to maintain communication via WhatsApp, email, or phone to resolve doubts and provide ongoing guidance. This approach ensures that patients are well-informed, supported, and able to make consistent progress in their health journey.
Conclusion: Holistic Naturopathy Approach for Lifestyle and Hormonal Health
The exploration of endocrine health, lifestyle diseases, diabetes management, and natural therapies underscores the importance of a holistic approach in achieving and maintaining optimal health. Across all discussions, one fundamental principle emerges: lifestyle is the foundation of health. Whether it is hormonal imbalances in women, Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, fatty liver, or high blood pressure, the quality and consistency of daily habits profoundly influence the body’s ability to heal, regenerate, and maintain balance.
In female hormonal disorders, naturopathy emphasizes root cause management, particularly addressing imbalances in Pitta and digestive health. Detoxification using herbs such as Triphala ensures that the digestive system functions efficiently, creating a favorable environment for hormonal regulation. Herbs like Ashokarishta, Rodra, Aloe Vera, and Shatavari act synergistically to regulate menstrual cycles, relieve menstrual cramps, and address hormonal infertility caused by imbalances. For growth and pituitary-related hormone disturbances, Ashwagandha, Shatavari, and Punarnava support endocrine function, improve metabolism, and assist in reducing inflammation naturally.
Lifestyle changes remain central to the management of metabolic and endocrine disorders. Consistency in sleep, meal timing, stress management, and daily routines supports the body’s circadian rhythm and metabolic cycles. Yoga and exercise, practiced even for 40 minutes daily, enhance circulation, flexibility, hormonal balance, and mental well-being. Simple postures such as Chakki Chalanasana, Malasana, Butterfly Pose, and Goddess Posture strengthen core and reproductive health while providing gentle stimulation to the endocrine glands. Hydrotherapy techniques like hot and cold water baths and magnet therapy further enhance detoxification and improve overall circulation.
In the context of diabetes, naturopathy provides realistic and sustainable strategies. While Type 1 diabetes cannot be reversed due to its autoimmune nature, natural therapies help minimize insulin dosage, support metabolism, and reduce complications. Type 2 diabetes, often linked with lifestyle, can be managed effectively with dietary regulation, exercise, and herbal supplementation. Herbs like Alfalfa, Wheatgrass, and Ashwagandha act as natural stabilizers, supporting glucose metabolism, enhancing immunity, and improving overall health. Moreover, these interventions help prevent complications such as fatty liver, high blood pressure, and cholesterol imbalances, which often coexist with diabetes as interconnected lifestyle diseases.
A key element in naturopathy is patient education and ongoing support. Patients benefit greatly when they understand the rationale behind each recommendation—from dietary modifications to herbal supplementation and exercise routines. Continuous guidance through consultations, messaging, or follow-ups ensures adherence and fosters a proactive attitude toward self-care. This patient-centric approach empowers individuals to make informed choices, gradually reduce dependence on allopathic medications, and actively participate in their healing process.
The integration of naturopathy with conventional medicine should be approached with care. Diagnostic tests such as CBC, ESR, and thyroid panels are essential to monitor progress and ensure safety while adjusting lifestyle or herbal interventions. Personalized recommendations based on age, symptoms, and individual constitution enhance the efficacy of treatments, minimizing risks of reverse effects or adverse reactions. Naturopathy recognizes that every patient is unique, and therapies must be tailored to their specific needs.
In conclusion, naturopathy emphasizes that true health restoration occurs when lifestyle, nutrition, herbal support, and mental well-being are addressed together. Hormonal balance, metabolic health, and chronic disease management cannot rely solely on medications; instead, they require a holistic, sustainable, and patient-centered approach. By adopting disciplined routines, mindful eating, therapeutic exercises, detoxification, and carefully selected herbs, individuals can experience gradual but profound improvements in their health.
Ultimately, naturopathy empowers patients to take responsibility for their own health, fosters natural healing mechanisms, and promotes long-term well-being. When lifestyle is controlled, stress is minimized, and the body is nourished with appropriate food and herbs, conditions such as hormonal imbalances, diabetes, fatty liver, and high blood pressure can be managed effectively. This approach is not only preventive but also restorative, offering patients the opportunity to live a balanced, healthy, and vibrant life naturally.