LIVER DISEASE
Understanding Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Overview
The liver, often referred to as the “chemical factory” of the body, is one of the largest and most vital organs in the human body. It plays a crucial role in maintaining overall bodily functions by producing enzymes, hormones, and other essential substances. This article delves into liver disease, exploring its root causes and how it progresses from initial stages to more advanced conditions.
The Core of Naturopathic Treatment:
In naturopathy, treatment is deeply rooted in the five elements of nature—earth, water, fire, air, and ether. These elements form the foundation of every naturopathic therapy. Regardless of whether a disease is in its early stages or has progressed to a more chronic state, the fundamental approach to treatment remains consistent. There is no need to alter the core principles of treatment based on the stage of the disease.
However, it’s essential to tailor the treatment to each individual. Factors such as age, the specific condition, and any related health issues must be considered. While the treatment approach stays the same, aspects like the duration of therapy and dietary recommendations may vary from person to person.
The Vital Functions of the Liver:
Understanding the liver’s role in the body is crucial to grasping how liver diseases develop and progress. Here are some of the key functions of the liver:
- Bile Production: Bile is essential for digestion, breaking down fats and aiding in the absorption of nutrients. A common saying, “Pet saaf toh rog maaf” (A clean stomach keeps diseases away), emphasizes the importance of proper digestion in preventing various diseases. If digestion is impaired, it can lead to a cascade of health issues.
- Excretion of Drugs, Hormones, Bilirubin, and Detoxification: The liver is responsible for excreting toxins, including drugs, hormones, and bilirubin. Proper excretion is vital for preventing the accumulation of harmful substances in the body, which can lead to various health problems.
- Metabolism of Fats, Carbohydrates, and Proteins: The liver plays a central role in metabolizing fats, carbohydrates, and proteins. For instance, carbohydrates from cooked food need to be metabolized effectively to provide energy for the body.
- Enzyme Activation: The liver is crucial for activating enzymes that are necessary for various bodily functions. Without proper enzyme activation, the body’s biochemical processes can be disrupted.
- Homeostasis Functions: The liver helps regulate blood glucose levels, which is particularly important for individuals with diabetes. If glycogen is not secreted properly, glucose can accumulate in the bloodstream, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
- Storage of Vitamins and Minerals: The liver stores essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12. These nutrients are crucial for maintaining overall health, and an imbalance can lead to deficiencies and related health issues.
- Synthesis of Plasma Proteins, Cholesterol, and Triglycerides: The liver synthesizes plasma proteins, cholesterol, and triglycerides, all of which are essential for cardiovascular health. An imbalance in these substances can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Liver Disease:Common Conditions

The liver is one of the most vital organs in the human body, often referred to as the “chemical factory” due to its essential role in maintaining overall body function. It is involved in digestion, metabolism, detoxification, and the regulation of various bodily processes. Weighing between 1.2 to 1.5 kilograms, the liver’s mass varies between individuals, often depending on factors such as gender and body structure.
Common Liver Diseases:
Research has identified several types of liver diseases, some of the most common being:
- Cirrhosis of the Liver
- Hepatitis B and C
- Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Liver Cancer
- Metabolism Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
- Jaundice
- Hemochromatosis
- Primary Biliary Cholangitis
- Cysts
- Alcoholic Liver Disease
- Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Cherry Syndrome)
- Gilbert Syndrome
- Hepatic Encephalopathy
- Wilson’s Disease
Among these, fatty liver disease is the most prevalent, affecting a significant portion of the global population. Many individuals with fatty liver disease are unaware of their condition, as it often presents no symptoms and is typically discovered during imaging tests for other health concerns.
Fatty Liver Disease: The Starting Point of Liver Problems
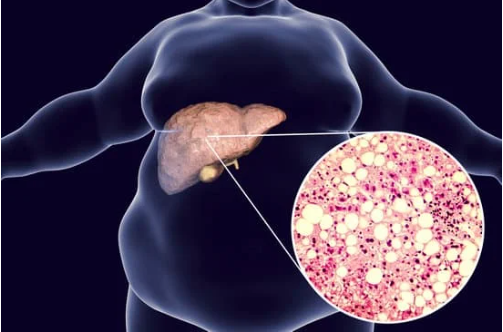
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. It can progress to more severe conditions such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), liver cirrhosis, and even liver failure if left untreated. Fatty liver is closely associated with conditions like central obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and insulin resistance. Regular monitoring of liver function through blood tests and sonography is essential for early detection and intervention.
Progression and Complications of Liver Disease:
The progression of liver disease from fatty liver to more severe conditions occurs gradually. Initially, fatty liver is marked by excessive fat accumulation, which impairs liver function. If unmanaged, this can lead to:
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A more severe form of fatty liver that involves inflammation and liver damage.
- Liver Cirrhosis: The advanced scarring of liver tissue, which significantly increases the risk of liver cancer.
- End-Stage Liver Disease: The final stage of liver disease, where the liver fails to function.
Common complications include:
- Swollen Veins in the Esophagus (Esophageal Varices): Increased pressure in the veins can lead to severe, life-threatening bleeding.
- Hepatic Encephalopathy: Elevated ammonia levels in the blood due to liver dysfunction can affect brain function, leading to confusion, drowsiness, and slurred speech.
Diagnosis and Management of Liver Disease:
Early diagnosis is crucial for managing liver disease. This typically involves blood tests, such as liver function tests, to assess liver enzymes and bilirubin levels, along with imaging tests like abdominal ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRIs. These tests help in identifying the extent of liver damage and guiding appropriate treatment.
Naturopathic Approach to Liver Disease:
Naturopathy emphasizes treating the root cause of liver disease rather than just the symptoms. For instance, in the case of fatty liver associated with obesity, the primary focus is on reducing weight and improving overall health through lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and exercise. Once obesity is managed, the liver condition often improves significantly.
Key aspects of the naturopathic approach include:
- Lifestyle Modification: Establishing a routine with proper sleep, regular meals, and adequate hydration can resolve many health issues.
- Dietary Changes: Reducing the intake of fats and carbohydrates while increasing protein can alleviate the burden on the liver.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, even simple exercises like walking or stretching, is crucial for reducing fat accumulation in the liver.
- Behavioral Modifications: Managing stress and anxiety is essential, as these can exacerbate liver dysfunction.
By focusing on these principles, naturopathy offers a holistic approach to managing and preventing liver disease, ensuring long-term health and well-being.
The Role of Liver Health in Overall Well-being
The liver is a vital organ responsible for various functions in the human body, from digestion and metabolism to detoxification and nutrient storage. Weighing between 1.2 to 1.5 kg, its mass varies between males and females, depending on body structure. Liver health is crucial as it plays a central role in managing the body’s metabolic processes and excretory functions. Despite its importance, many people are unaware of the various liver diseases that can develop, often silently.
Common Liver Diseases:
Liver diseases range from cirrhosis and hepatitis to autoimmune conditions and liver cancer. One of the most prevalent issues is fatty liver disease, which affects a significant portion of the global population. Fatty liver is often asymptomatic, making it challenging to diagnose without specific imaging tests like ultrasounds or sonography. It is commonly linked to central obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and insulin resistance.
The Importance of Early Detection:
Fatty liver disease can progress to more severe conditions like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), liver cirrhosis, and even liver failure if left untreated. Early detection through blood tests and imaging is crucial for preventing complications. Symptoms like abdominal pain, swelling, jaundice, and mood fluctuations can indicate liver issues. If these symptoms persist for over a month, it is advisable to consult a doctor and get the necessary tests done.
Behavioral Modification and Diet Recommendations:
Behavioral modification is essential for managing liver disorders. Incorporating specific techniques for 10 to 15 minutes daily can help address issues like negativity, short temper, and impatience, which can burden the liver.
Dietary Recommendations:
- Reduce Fat: Focus on fat reduction rather than extreme weight loss to maintain health and nutrient levels. Consulting a dietitian is advisable.
- Avoid Extreme Diets: Steer clear of extreme diets like zero-carb or keto diets, which may not be suitable for everyone. Instead, incorporate antioxidant-rich foods like fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Essential Foods: Include foods like bitter gourd, garlic, walnuts, and broccoli in your diet. These natural remedies can help with insulin resistance and cardiovascular issues, while also supporting liver health.
- Herbs: Utilize herbs like Punarnava and Giloy, known for their liver-regenerating properties. These can be consumed fresh or in powdered form, available at Ayurvedic stores.
Case Study-The Impact of Lifestyle Changes:
A 40-year-old patient with grade three fatty liver and obesity saw significant improvement within 60 days through lifestyle and dietary changes. Follow-up tests showed normalized liver function, demonstrating the effectiveness of these interventions.
Yogasanas for Liver Health: A Naturopathic Perspective

Liver health is crucial for the overall well-being of the body, and certain yogasanas can play a significant role in regenerating the liver and controlling bile secretions. Here are some scientifically proven asanas that can help improve liver function:
Paschimottanasana: Stimulating the Liver:
Paschimottanasana is a forward bend that stimulates the liver and promotes blood circulation to this vital organ. The asana helps to rejuvenate liver cells, encouraging the secretion of bile and supporting the liver’s overall health.
Ekpada Pavanmuktasana: Aiding Digestion:
Ekpada Pavanmuktasana is particularly beneficial for those suffering from fatty liver, especially in cases of Grade 3 or more severe damage. This asana aids in digestion, helping to reduce the load on the liver and supporting its regeneration.
Ardha Matsyendrasana: Promoting Detoxification:
Ardha Matsyendrasana is a twisting pose that massages the liver and pancreas, promoting detoxification and enhancing liver function. Regular practice of this asana can help cleanse the liver, improving its ability to filter toxins from the body.
Savasana: Relaxation and Regeneration:
Savasana, also known as the corpse pose, is one of the simplest and most accessible asanas. It can be performed at any stage of life and by people of all ages. Savasana promotes deep relaxation, allowing the liver to regenerate and function optimally.
These yogasanas, when practiced regularly, can greatly benefit liver health. Incorporating them into your daily routine can support the liver’s natural processes, aiding in detoxification and overall well-being.
Effective Naturopathy Therapies for Detoxification and Liver Health

In naturopathy, there are several therapies available that can help treat patients through detoxification and other natural methods. Below are some of the key therapies and practices that can be utilized:
Detox Therapy through Fasting:
Detoxification can be achieved in various ways, one of the most effective being fasting. Fasting can be approached differently depending on the patient’s condition and needs. Here are some common types of fasting:
- Mono Diet: Consuming a single type of food.
- Liquid Diet: Fasting with liquids only.
- Raw Diet: Consuming only raw foods.
- Warm Water Fasting: Drinking only warm water.
Even patients with conditions like diabetes, who often believe they cannot fast, can safely undergo fasting therapy. Fasting can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve HbA1c. However, it’s essential to tailor the fasting method to the patient’s age, health condition, and other factors. Proper guidance on how to start, maintain, and break the fast is crucial.
Enema Therapy for Detoxification:
Enema is another detoxification method that can be recommended monthly for at least three consecutive days. The most common enema uses warm water with lemon. Depending on the patient’s constitution (prakruti), enemas can be enhanced using buttermilk or fresh herbal juices like neem. This therapy helps cleanse the digestive system and supports liver health.
Steam Bath Therapy:
Steam baths are a valuable detoxification tool that should be done for 5 to 7 minutes, depending on the patient’s capacity. It aids in opening pores, eliminating toxins through sweat, and improving circulation.
Gastro-Hepatic Pack Therapy:
The gastro-hepatic pack, also known as the hot and cold pack, is a simple but effective therapy. It involves placing a hot water bag on the stomach and a cold (gel) bag on the back for 30 minutes on an empty stomach. This therapy should be continued for 60 days to see significant benefits in liver function.
Tub Bath Therapy:
Tub bath therapy is another beneficial practice, alternating between 10 minutes of warm water and 10 minutes of cold water. This therapy, like the gastro-hepatic pack, should be performed on an empty stomach for 60 consecutive days. It helps improve circulation and supports detoxification.
Sunbath Therapy:
Sunbathing is a natural way to boost vitamin D levels, essential for liver function and bone health. It also provides fresh air and oxygen, which are vital for overall well-being.
Dietary Tips for Liver Health

In addition to these therapies, certain dietary practices can significantly support liver health:
- Bittergourd Juice: This powerful liver stimulant helps combat fatty liver disease by detoxifying liver enzymes and breaking down fatty molecules. Fresh bittergourd juice is preferable over cooked preparations.
- Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa): If available, this herb is excellent for detoxification and liver regeneration. Punarnava tea or decoction can be prepared for its anti-inflammatory and liver-supportive properties.
- Hydration: Regularly hydrating the body is crucial for liver health. It’s important not to overeat and to ensure that the stomach is only 80% full during meals, leaving 20% empty to aid digestion and absorption.
Additional Lifestyle Tips:
- Mindful Eating: Encourage patients to eat slowly, mixing saliva with food properly. Drinking water in small sips rather than gulping it down can prevent digestive strain and improve overall digestion and metabolism.
- Symptom Management: Advise patients not to neglect any symptoms. Early treatment and observation are key to preventing disease progression and preserving organ health.
Incorporating these therapies and lifestyle changes into daily routines can help patients achieve better health outcomes and prevent the onset of diseases. By following these naturopathic principles, patients can support their liver and overall well-being naturally.