SKIN DISEASE
Urticaria and Hives: Types, Causes, and Symptoms
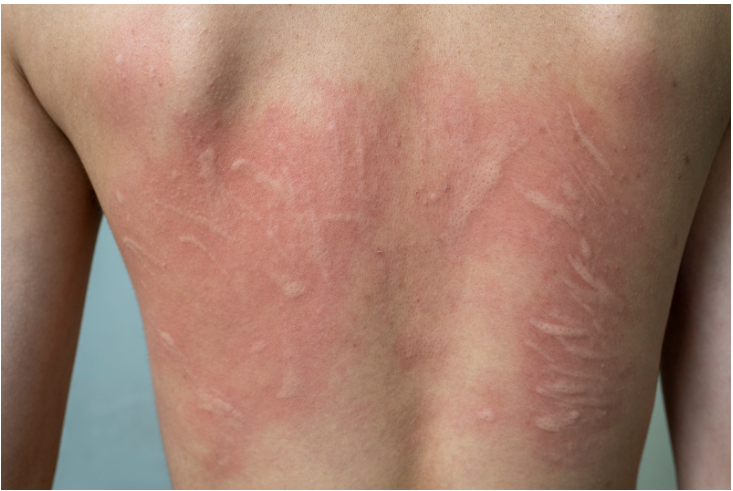
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a prevalent skin condition characterized by red, raised patches that cause itching or burning sensations. These patches, also referred to as welts or wheals, appear due to various factors, such as allergies, infections, or even emotional stress. Let’s delve into the definition, types, and causes of Urticaria.
What is Urticaria?
The term “Urticaria” is derived from the Latin word for “burn,” as the condition often results in a burning sensation on the skin. It is also referred to by several other names, including hives, welts, wheals, and nettle rash. Urticaria manifests as a skin rash that typically consists of red, raised, itchy bumps on the surface of the skin. In severe cases, the rash may resemble small blood spots scattered across the affected area.
Urticaria is commonly triggered by allergens such as certain foods, drugs, infections, and even emotional disorders. It is frequently observed in children and adults, particularly women aged 32-60.
Types of Urticaria:
There are various types of Urticaria, categorized based on duration, severity, and treatment approaches. The most common forms include:
- Acute Urticaria: This is the most frequent type of Urticaria, often seen in children or adults following an insect bite or exposure to a substance they are sensitive to. Acute Urticaria is typically short-term, lasting only a few hours to a few days, and can usually be treated with home remedies. It is characterized by mild itchiness and pale bumps on the skin, often on the hands or legs.
- Chronic Urticaria: Unlike acute Urticaria, chronic Urticaria can last for months or even years. It requires ongoing treatment, often with antihistamines, to manage the symptoms. In some cases, chronic Urticaria may last for 15-20 years and, in rare instances, can be life-threatening.
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: This type of Urticaria does not have a known cause but is thought to be triggered by similar factors as other forms of Urticaria, such as medications, infections, or underlying diseases.
- Physical Urticaria: This type occurs in response to physical stimuli such as extreme cold or heat, sun exposure, or pressure on the skin. It can also be triggered by vibrations or environmental changes.
- Urticaria Factitia: This form of Urticaria is caused by skin friction, such as rubbing or scratching, tight clothing, or repeated physical contact with a specific area of the body. People experiencing Urticaria Factitia may notice red patches or welts after engaging in such activities.
- Cholinergic Urticaria: This type is triggered by physical exertion or an increase in body temperature, such as from exercise, fever, or hot baths. Some individuals are particularly sensitive to even small rises in body temperature, resulting in an Urticaria outbreak.
- Aquagenic Urticaria: As the name suggests, this type is caused by water exposure. People who frequently change environments and experience water changes may be prone to this condition. Contaminants in water can also be a trigger for aquagenic Urticaria.
Causes of Urticaria:
Urticaria can be triggered by a wide range of factors, including:
- Foods: Certain foods, such as shellfish, nuts, eggs, and dairy products, are common allergens that may lead to Urticaria.
- Medications: Antibiotics, aspirin, and other medications may trigger hives in sensitive individuals.
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections can sometimes result in Urticaria.
- Physical stimuli: Heat, cold, pressure, or sun exposure can cause hives in some people.
- Emotional stress: Psychological factors can also play a role in triggering Urticaria in certain cases.
Urticaria, while common, can present itself in various forms, ranging from mild and short-lived to chronic and life-threatening. Recognizing the different types and causes of Urticaria is crucial for effective management and treatment. Whether it’s acute or chronic, consulting a healthcare provider can help determine the best course of action to manage the condition and provide relief.
Understanding Urticaria: Symptoms, Types, and Common Triggers
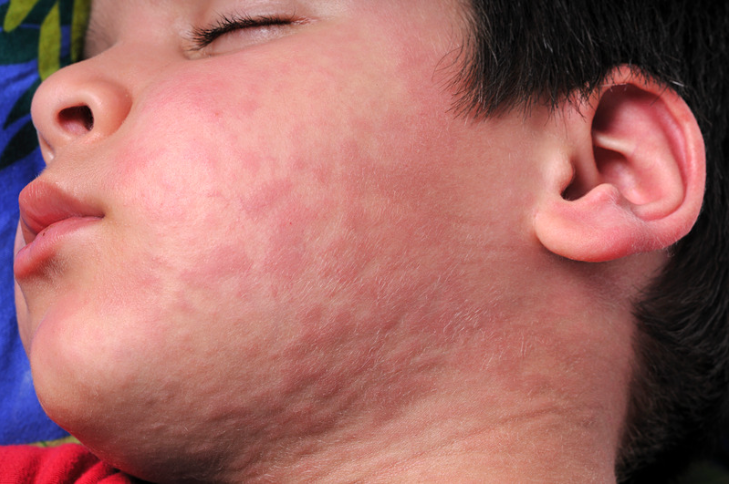
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition that causes raised, itchy bumps on the surface of the skin. These bumps can range in size from small pinpricks to several inches across. The appearance of hives is often sudden and can be caused by various triggers. In this article, we will explore the symptoms of urticaria, different types of hives, and how it affects individuals.
Types of Urticaria:
Urticaria comes in various forms, each with distinct characteristics. The bumps, or hives, are typically pink, red, or skin-colored and can appear as:
- Pinprick-sized bumps: Small and scattered over the body, resembling tiny drops of blood.
- Larger bumps: When several small hives join together, forming bigger raised areas on the skin.
The color of these hives may change based on pressure. For instance, they can appear pale when pressed and usually disappear within 24 hours. However, they can reappear just as quickly, triggered by a reaction to certain foods, products, or allergens.
Symptoms of Urticaria:
The most common symptom of urticaria is the appearance of raised, itchy bumps on the skin. These can vary in shape, such as:
- Tiny spots
- Blotches
- Thin, raised lines
In some cases, the appearance of hives can change depending on the severity of the scratching. The bumps might merge to form larger lesions, especially when triggered by a food allergy. In such cases, the reaction can disappear within an hour, while hives caused by additives or food coloring may last longer, sometimes up to 24 hours. Individuals with severe allergies may need medication, and in chronic cases, the condition can persist for months or even years, requiring ongoing treatment.
The Nature of Urticaria:
Hives can take different shapes, such as rings or lines, and may have prominent, well-defined edges. These bumps may disappear and reappear, making the condition unpredictable. In fact, most people experience hives at least once in their lives, especially during the summer or winter months. It is not uncommon to notice them on areas like the stomach, thighs, or legs, often caused by pressure from clothing, such as tight socks or jeans.
Chronic Urticaria:
For some individuals, hives may last for several days or even months. Chronic hives may persist for years, causing discomfort and requiring long-term medication. The itching and swelling are key symptoms, and the raised welts, known as wheels, can grow larger over time. These wheels often merge together, forming larger raised areas that can last for hours before disappearing, only to reappear in different areas.
Dermatographism: A Unique Form of Hives:
One specific type of urticaria is dermatographism, also known as skin writing. This form of hives occurs when pressure is applied to the skin, causing immediate raised welts in that area. These hives can be triggered by scratching or pressing on the skin and are one of the most common types of physical urticaria.
Urticaria, or hives, is a common skin condition that affects many people at least once in their lives. While the symptoms can range from mild to severe, most cases are temporary and resolve within hours or days. However, in chronic cases, it can last for years and may require ongoing treatment. Understanding the triggers and symptoms of urticaria is essential for managing and alleviating discomfort associated with this condition.
Urticaria: Causes, Triggers, and Treatment:
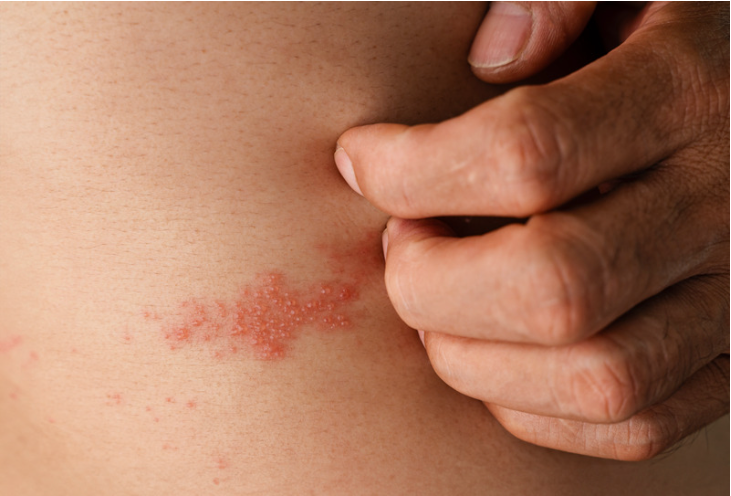
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by red, itchy welts that can appear suddenly. It can be triggered by various factors, including allergens, physical stimuli, infections, or underlying health conditions. In this article, we’ll explore the different causes of urticaria, how it manifests, and what steps can be taken for effective treatment.
1. Common Causes of Urticaria:
The triggers for urticaria are diverse, and they can be both internal and external. Some of the common causes include:
Allergens:
- Food Allergies: Common food allergens such as nuts, eggs, and seafood can trigger hives. Consuming or even touching certain foods can cause an allergic reaction, resulting in red, itchy bumps on the skin.
- Insect Bites: Stings or bites from insects like ants or mosquitoes can lead to urticaria, especially in individuals with heightened sensitivity to these allergens.
- Pollen and Dust: Exposure to environmental allergens such as dust mites, pollen, or pet dander can also lead to hives.
Physical Triggers:
- Pressure or Friction: Tight clothing, belts, or any form of pressure on the skin can induce hives. This is common in areas where the skin is rubbed or compressed.
- Extreme Temperatures: Sudden changes in temperature, extreme heat, or cold can cause the skin to react by forming welts.
- Sunlight Exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV light from the sun or tanning beds can trigger urticaria in sensitive individuals.
Infections and Medications:
- Viral Infections: Urticaria can sometimes be triggered by infections such as the flu, common cold, or hepatitis B.
- Medications: Certain drugs, particularly non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin, or blood pressure medications such as angiotensin inhibitors, can also lead to hives in some individuals.
Underlying Health Conditions:
- Autoimmune Disorders: In some cases, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, thinking they are foreign invaders. This can lead to autoimmune conditions such as autoimmune hypothyroidism, which can also manifest as urticaria.
- Thyroid Disorders: People with hypothyroidism, particularly those with autoimmune hypothyroidism, may experience urticaria as a symptom. This occurs when the immune system misidentifies healthy tissues and starts attacking them, resulting in various autoimmune reactions.
2. How Urticaria Develops:
When the body comes into contact with an allergen, it releases histamine. This histamine, which leaks through the capillaries, causes fluid to accumulate in the skin, leading to the formation of red, itchy welts. These hives may appear on any part of the body and can last for varying durations, from a few minutes to several hours or even days.
The severity of the reaction can vary depending on the individual’s sensitivity to the allergen. In some cases, the hives may be mild and fade quickly, while in others, the reaction may be more intense and require medical intervention.
3. Physical and Environmental Triggers:
Besides allergens, certain physical and environmental factors can also trigger urticaria. These include:
- Sweating and Exercise: Excessive sweating, particularly during or after exercise, can cause hives due to increased body temperature.
- Tight Clothing: Wearing tight belts, leggings, or other restrictive clothing can trigger pressure hives.
- Heat and Cold: Extreme changes in temperature, including hot showers or exposure to cold air, can also provoke urticaria in sensitive individuals.
4. Treatment and Management of Urticaria:
The first step in treating urticaria is identifying and avoiding triggers. If food or environmental allergens are the cause, eliminating or reducing exposure to these allergens can help prevent future outbreaks. In the case of physical triggers, such as pressure or extreme temperatures, individuals should modify their activities or clothing choices to minimize their impact.
Medications, particularly antihistamines, are commonly used to manage the symptoms of urticaria. These drugs work by blocking the effects of histamine, thereby reducing itching, redness, and swelling. In more severe cases, corticosteroids or other medications may be prescribed by a healthcare provider to help control the condition.
If the urticaria is caused by an underlying health condition, such as an autoimmune disorder, treating the primary condition may also alleviate the symptoms of hives.
5. When to Seek Medical Help:
While most cases of urticaria are mild and resolve on their own, certain situations require immediate medical attention. If the hives are accompanied by difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or other signs of anaphylaxis, seek emergency medical care.
Additionally, if the hives persist for more than six weeks, it may be a sign of chronic urticaria, which requires a more thorough medical evaluation and treatment plan.
Urticaria, though common, can be a distressing condition, particularly for individuals who experience frequent outbreaks. Understanding the various causes and triggers is key to managing and preventing hives. By identifying allergens, avoiding physical triggers, and seeking appropriate medical care when necessary, individuals can significantly reduce the impact of urticaria on their daily lives.
For anyone experiencing persistent or severe symptoms, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Ayurvedic Home Remedies and Home Care Strategies for Urticaria
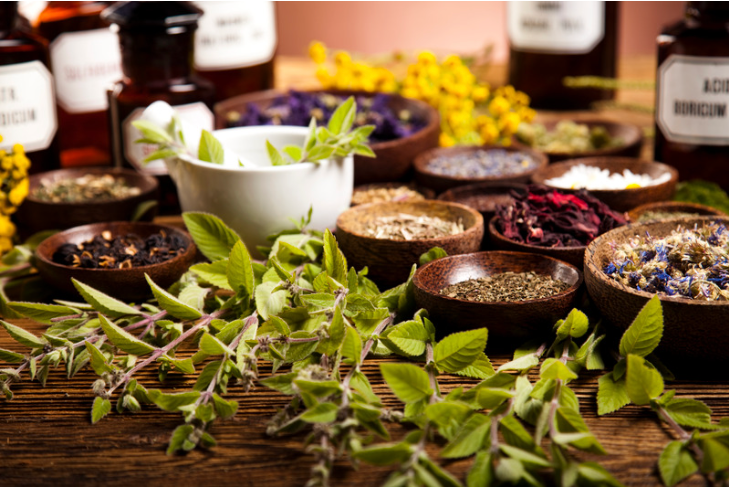

Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a condition that causes red, itchy welts on the skin. It can occur due to various triggers such as food, environmental allergens, medications, or even stress. While medications are often required for severe cases, acute urticaria can be effectively managed using home remedies and natural treatments. Ayurveda, naturopathy, and homeopathy offer various remedies to ease the symptoms and promote healing. In this article, we will explore Ayurvedic home remedies and essential home care strategies for managing acute urticaria.
Ayurvedic Home Remedies:
Ayurveda provides several remedies that help manage the symptoms of acute urticaria. These natural ingredients offer relief and healing without the harsh side effects often associated with medications. Some of the most effective Ayurvedic remedies include:
- Aloe Vera Pulp: Known for its cooling properties, aloe vera pulp helps soothe irritated skin and reduce the redness and itching caused by urticaria.
- Neem Leaf Paste: Neem is a natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent. Applying a paste made from fresh neem leaves can help calm the itching and speed up the healing process.
- Mustard Oil and Black Pepper: A mixture of mustard oil and black pepper can be applied to the affected areas to reduce itching and inflammation.
- Desi Ghee and Honey: Both desi ghee and honey are commonly used in Ayurveda to promote skin healing. They can be applied topically or consumed to strengthen the body’s immunity against allergic reactions.
- Split Legumes, Pomegranate Juice, and Amla Juice: Consuming these foods can help detoxify the body and reduce the internal inflammation that often triggers urticaria.
These remedies are best suited for cases where the urticaria is not caused by underlying health conditions, and when the flare-ups are limited to external physical factors.
Home Care Strategies for Acute Urticaria:
Along with Ayurvedic treatments, adopting the right home care strategies can help in managing urticaria more effectively. Here are some key steps to follow:
1. Maintain a Symptom Diary:
One of the first steps in managing urticaria is keeping a detailed diary of symptoms. This includes tracking your diet, stress levels, activity, and environmental exposure. By maintaining a 24-hour or one-week recall, both the patient and healthcare provider can better understand potential triggers, such as specific foods, clothing materials, or environmental allergens.
2. Monitor Triggers:
Careful monitoring of potential allergens is crucial in identifying the root cause of urticaria. For instance, food-related allergies may cause flare-ups within 1-2 hours of consumption, or sometimes even after 12-24 hours. On the other hand, exposure to allergens like pollen or dust may trigger immediate reactions, such as itching or red welts within 10 minutes. Observing your reaction to various items over a period of 10-15 days can help pinpoint the allergens and guide effective treatment.
3. Hygiene Maintenance:
Good hygiene plays a vital role in preventing the worsening of urticaria. Key points to keep in mind include:
- Change clothes, towels, and personal belongings frequently. Items like undergarments and towels should be replaced every 3 to 5 months.
- Ensure daily washing of clothes and towels to keep them clean.
- Avoid sharing towels and personal items with others to prevent cross-contamination.
Maintaining hygiene not only helps in soothing the symptoms but also prevents the spread of irritants that could worsen the condition.
4. Bathing and Cooling Strategies:
Taking cool showers and using chemical-free, natural soap is highly recommended. Adding specific naturopathic ingredients to bathwater can provide relief from the burning and itching caused by urticaria. Cool compresses can also help soothe the skin, especially if you are not allergic to cold stimuli.
However, it’s essential to avoid squeezing or scratching the welts or hives, as this can cause wounds and delay healing.
5. Personal Care Products:
When managing urticaria, choosing the right personal care products is crucial. Avoid products containing chemicals or harsh ingredients that can irritate the skin. Opt for natural, mild shampoos and soaps. Also, avoid alcohol-based products that dry out the skin.
6. Clothing Choices:
Wear loose-fitting clothes made from natural fabrics like cotton that allow the skin to breathe. Synthetic fabrics can aggravate the symptoms and worsen the flare-ups, so it’s important to stick to breathable, comfortable clothing.
Managing acute urticaria can be achieved through a combination of Ayurvedic remedies and careful attention to home care practices. By following these strategies, patients can experience relief from the itching and discomfort associated with the condition. Maintaining hygiene, monitoring potential allergens, and using natural remedies can make a significant difference in managing and preventing further flare-ups. Always consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and to ensure that you are using the best treatment plan suited to your needs.
Lifestyle and Dietary Recommendations for Urticaria Relief
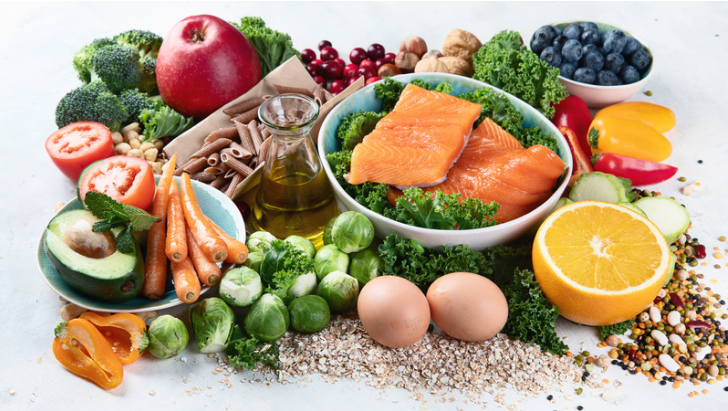

Understanding Urticaria and the Importance of Nutrition:
When dealing with urticaria, maintaining a well-balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals is crucial. Since urticaria is an immune disorder, boosting immunity and reducing inflammation through diet can significantly help in managing the symptoms. Vitamins such as C, E, and K, along with minerals like zinc, selenium, iron, and calcium, are key components for promoting healing and supporting overall health.
A proper dietary plan not only helps in managing urticaria but also strengthens the body’s defenses, thanks to the antioxidant-rich foods that play a vital role in combating immune-related issues.
Key Nutrients to Incorporate:
- Vitamin C, E, and K: These vitamins act as powerful antioxidants that help in boosting immunity and repairing skin damage caused by urticaria. They can be found in various fruits and vegetables that are easy to incorporate into your daily meals.
- Zinc, Selenium, and Iron: These minerals help in maintaining skin health and regulating immune responses, thus reducing flare-ups.
- Calcium-Rich Foods: Ensuring adequate calcium intake supports overall health and contributes to skin healing.
- Food Allergy Awareness: Identifying and addressing food allergies is crucial. It is recommended to observe your diet over a period of one week to ten days to determine if specific foods are triggering allergic reactions. Pay attention to any signs of intolerance and avoid consuming food additives.
Foods to Avoid:
Certain food additives can aggravate urticaria. Common additives such as Allura Red, Sodium Benzoate, and Tetrazine (FD&C Yellow) are known to trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Avoiding processed foods and artificial ingredients can help prevent chronic symptoms from worsening over time.
Hydration and Exercise:
Proper hydration is essential to flush out toxins from the body, which can alleviate urticaria symptoms. Drinking adequate amounts of water throughout the day supports detoxification and improves skin health.
Exercise is also beneficial but should be mild and non-strenuous. Avoid engaging in intense physical activities that may exacerbate symptoms. Maintaining an active lifestyle with light exercise can improve overall well-being without adding stress to the body.
Rest and Sleep:
Good quality sleep is one of the most important lifestyle factors in managing urticaria. A restful night’s sleep promotes healing and helps the body recover from flare-ups, reducing both physical and emotional stress.
Naturopathic Therapies for Urticaria

In addition to dietary adjustments, various naturopathic therapies are beneficial for treating urticaria. These therapies complement a healthy diet and provide relief from symptoms such as itching, swelling, and inflammation.
1. Mud Therapy:
Mud therapy is a soothing option that can help alleviate itching and reduce swelling associated with urticaria. It is a natural remedy that draws out toxins and provides immediate relief.
2. Sun Therapy:
Sun therapy can be beneficial, but it should be avoided if the individual has sun-induced urticaria. For those without sun sensitivity, moderate sun exposure can help improve skin conditions and boost Vitamin D levels.
3. Cold Compresses:
Cold compresses are effective in relieving the intense itching and burning sensations that accompany urticaria. Regular application can soothe the skin and reduce the severity of flare-ups.
4. Fiber Intake and Constipation:
People with urticaria often consume less fiber due to discomfort, which can lead to constipation. It’s important to maintain regular bowel movements to flush out toxins from the body. Fiber-rich foods should be included in the diet, especially during flare-ups, to aid digestion.
Supplements and Botanical Remedies:
In addition to diet and therapies, supplements can support the body’s healing process. Key supplements include:
- Essential Fatty Acids (such as Omega-3s)
- DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone)
- Betaine HCL
- Digestive Enzymes
- Probiotics
These supplements support digestion, enhance immunity, and promote overall well-being. Certain botanical remedies like feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium) and nettle (Urtica dioica) are also helpful in managing the symptoms of urticaria.
1. Gemmo Therapy:
This therapy involves the use of plant buds for healing. For urticaria, gemmo remedies such as Alnus Glutinosa and Platanus Orientalis can be used.
2. Homeopathy:
Homeopathic remedies like Apis, Arsenicum, Dulcamara, Pulsatilla, Rhus Tox, and Sepia can provide relief from the chronic symptoms of urticaria.
Foods to Eat:
To ensure proper nourishment and avoid nutrient deficiencies, it’s important to consume a wide variety of foods rich in essential vitamins and minerals. Some of the most beneficial foods include:
- Vitamin B5: Whole wheat, pasta, breads, hazelnuts, chickpeas, eggs, mushrooms, and rye.
- Vitamin C: Blackberries, cherries, asparagus, cantaloupe, avocado, grapefruit, papaya, oranges, and lemons.
- Vitamin E: Cold-pressed olive oil, kelp, kale, pumpkins, seeds, and almonds.
Incorporating these nutrient-dense foods into your diet will help combat the deficiencies caused by urticaria and promote skin health.
By following a holistic approach that includes a nutrient-rich diet, proper hydration, gentle exercise, and naturopathic therapies, individuals with urticaria can manage their symptoms effectively. Addressing both lifestyle and dietary changes is crucial for long-term relief from this immune disorder.
Managing Urticaria (Hives): A Comprehensive Guide
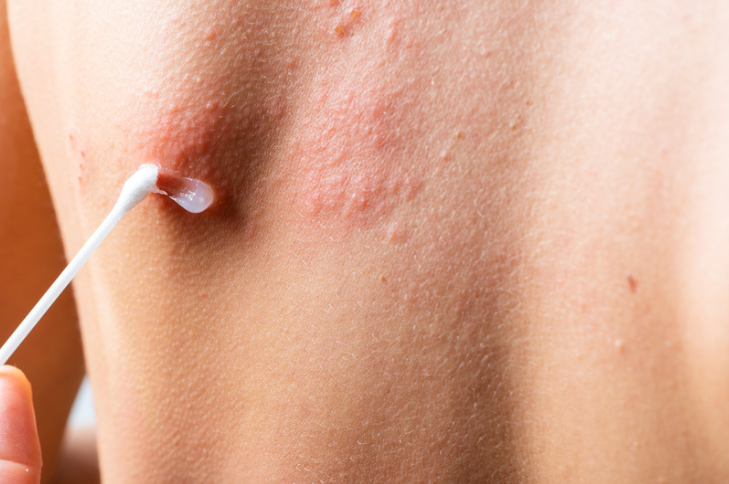
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by red, itchy welts or hives that can appear suddenly and often cause significant discomfort. It is important to treat this condition effectively, keeping in mind several key strategies. Here’s a detailed guide on managing and treating urticaria.
Foods to Avoid in Urticaria:
When dealing with urticaria, it’s essential to identify and eliminate any food triggers. Start by understanding the client’s allergies, and avoid specific foods that may worsen the condition. Foods to avoid include:
- Alcohol and Caffeinated Drinks
- Processed foods, half-cooked foods, and histamine-containing foodslike:
- Cheese, yogurt, buttermilk
- Shellfish, fish, eggs
- Chocolate, aged foods, fermented foods
- Artificial food colorings
- Processed meats, berries, tomatoes, and wheat
It is crucial to keep track of any food that the client is allergic to and avoid it completely.
Managing Urticaria with Stress Reduction and Lifestyle Changes:
In addition to eliminating food triggers, a calm environment and proper counseling are essential. Here’s how to manage stress and soothe the skin:
- Counseling and Support: It’s important to be patient and understanding with clients suffering from urticaria. Counseling them through their discomfort, creating a friendly environment, and avoiding irritability can help the client feel more comfortable.
- Calming the Skin: Cold compresses and calming treatments like an oatmeal bath can relieve itching. Oatmeal has soothing properties that calm the skin. You can use colloidal oatmeal, available in the market, by adding it to bath water or using rolled oats by blending them into a fine powder and adding it to water. Another option is to place the oats in a muslin cloth bag and dip it into the bathwater for a soothing effect.
- Baking Soda for Relief: Baking soda is another effective treatment. Mix it with water and apply it to the affected areas, or add it to the bathwater for a soothing soak. This helps calm inflammation and itching.
- Witch Hazel: Witch hazel, available in the market, can also provide relief. It can be applied as a mask on the affected areas, or a general application can be made over the whole body. For areas like legs and arms that may be covered in hives, applying witch hazel and letting it sit for about 20 minutes before rinsing can help soothe the skin.
Supplements to Include for Healing:
Due to poor dietary intake during urticaria, clients may experience deficiencies in vitamins, leading to symptoms like constipation and weakness. It is essential to address these deficiencies by supplementing with:
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin C (1000 mg three times a day is highly recommended)
These vitamins help combat the symptoms of urticaria and strengthen the immune system, assisting in a quicker recovery.
Acupuncture for Urticaria:
Acupuncture is another treatment option for calming the symptoms of urticaria. It is an alternative therapy that focuses on inserting needles into specific points of the body to relieve inflammation and stress. It can be particularly effective in reducing the body’s overall response to hives and soothing skin irritation.
Diagnostic Tests for Urticaria:
When seeking medical help, the doctor may recommend various tests to diagnose the severity of urticaria:
- Scratch Test or Skin Prick Test: These tests help identify specific allergens.
- Blood Tests: To check for antibodies associated with allergic reactions.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): High levels of ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate) can indicate inflammation. A high ESR can occur during acute flare-ups of urticaria but should subside with treatment.
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Test: To check for active inflammation in the body.
- Serum Skin Test: A simple diagnostic test to assess allergic reactions in the skin.
Managing urticaria requires a multifaceted approach that includes dietary adjustments, stress management, soothing treatments, and medical interventions. With proper care and understanding, clients can find relief from the itching, redness, and discomfort associated with urticaria. If the symptoms persist or worsen, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for further evaluation and treatment.