SPINE & CERVICAL SPINE
SPINE & CERVICAL SPINE
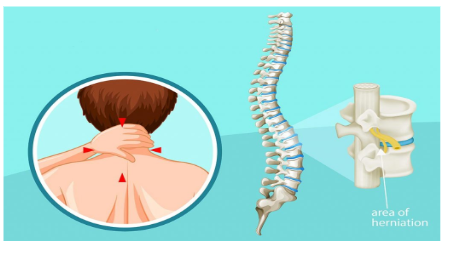
The spine or backbone is bony structure that supports our body to sit, stand, walk, twist and bend. The three primary roles of the spinal cord are to send motor commands from the brain to the body, send sensory information from the body to the brain, and coordinate reflexes.
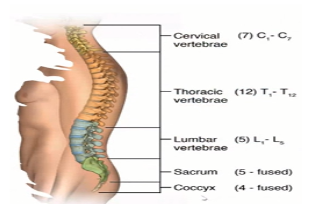
The spine has 33 stacked vertebrae (small bones) that form the spinal canal. The spinal canal is a tunnel that houses your spinal cord and nerves, protecting them from injury.
Cervical spine is the top part of your spine, has seven vertebrae (C1 to C7). These neck vertebrae allow you to turn, tilt and nod your head, also provides support for the weight of your head. Many conditions affect this area of spine including neck pain, arthritis, degenerative bone and disk disease and stenosis.
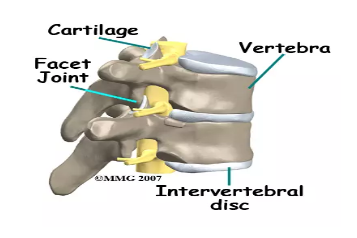
The intervertebral discs are complex structures that consist of a thick outer ring of fibrous cartilage termed the annulus fibrosus, which surrounds a more gelatinous core known as the nucleus pulposus; the nucleus pulposus is sandwiched inferiorly and superiorly by cartilage end-plates.
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS
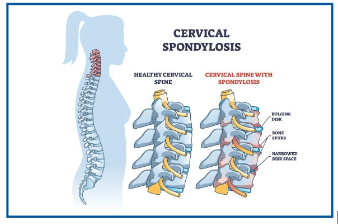
Cervical spondylosis is the medical term for neck pain caused by age related degeneration of cervical region of the spine. Research shows that 80 percent of all people 40 years and older show signs of spondylosis on an x-ray examination. Doctors believe the majority of cases are associated with genetics and injury. After the age of 60years, cervical spondylosis affects more than 90% of population.
It results from degeneration of intervertebral disc and consequent pressure on the cervical nerve roots at cervical spinal cord.
SYMPTOMS OF SPONDYLOSIS
Nagging & Severe Neck Pain
Acute or Chronic Stiffness Numbness and tingling or complete loss of sensation
Headache
Giddiness
Muscle weakness of the arm of the hand
Neck pain spreads to shoulders and base of the skull
Neck movement worsens pain
Pain flare- ups from time to time
Persistent neck pain
Neck stiffness, particularly after a night’s rest
Headaches start at back of the head and travel to forehead Pain spreading down the arm to the hand or fingers
Tingling in a part of an arm or hand
Numbness or weakness in a part of a hand or arm
CAUSES
Age
Injury
Faulty Posture
Psychological Strain
Lack of exercise
Ergonomics
Improper lifting of the weights
Genetics
Incorrect Nutrition
Injury like whiplash
Physical strain
Mental stress
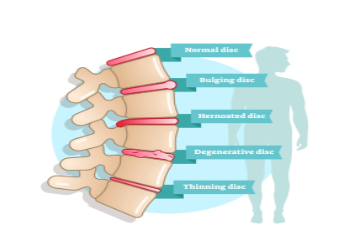
SLIP DISC VS SPONDYLOSIS
Slip disc, also called a prolapsed or herniated disc, is a condition where the spine disc or a soft cushion of tissue between the bones is moved out of its position. It usually gets better slowly with rest, gentle exercise and pain killers. Whereas Spondylosis is the degeneration of the bones and disks. Spondylosis can be quite painful and even cause disability with compression of nerves or the spinal cord.
TREATMENT & SAFETY MEASURES
Treatment – Medications (NSAID’s), cervical collar, corticosteroid injections, physiotherapy and sometimes spinal surgery
Stay active but avoid doing activities that put pressure on the neck.
Avoid lifting heavy weights.
Take short breaks in between work to give rest to the neck.
Stay hydrated.
Exercise regularly, but with caution and care.
Eat healthy food-Eat fruits and green leafy vegetables
Maintain a healthy weight
Remember your posture
Sleep properly, avoid or use thin pillows
Quit smoking
YOGA & EXERCISE
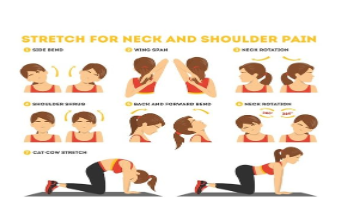
Exercises that improve the supply of nutrients to spinal discs
Joint movements-fingers, wrists, forearms and shoulder rotations, head & neck movements.
Stand up and move around every hour
Changing position in sitting jobs
Sleeping on the sides with knees bent on firm mattress
Yoga asanas that help in alleviating the pain:-
Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose)
Ardha Matsyendrasana (Sitting Half-Spinal Twist)
Dhanurasana (Bow Pose)
Marjariasana (Cat Pose)
Setu Bandhasana (Bridge Pose)
Matsyasana (Fish Pose)
NATURE’s CURE TO THE RESCUE
Fire – Heliotherapy – Sun exposure (after applying the oil) The oil is prepared by frying 10 cloves of garlic in 60gm of oil at a low flame, till they are brown. After it is cooled, it should be applied vigorously on the affected part & allow it to remain for 3 hrs. Or apply warm coconut or mustard oil mixed with camphor
Earth –
Mud pack on abdominal area.
Diet should consist of lot of vegetables and fruits. Also adequate amount of proteins, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Calcium, phosphorus, omega 3 and other trace elements are necessary for healthy bones.
Space – Periodic fasting and regular Intermittent fasting is beneficial for reducing the severity of chronic inflammation
Air-Pranayama – Nadishuddhi, Suryabhedana and Bhramari, Om chanting, Breath awareness and Om meditation
HYDROTHERAPY
Applying wet pack
Hot fomentation for 5-10mins twice a day
Spinal bath – Relax for 30mins every night in a tub of water with a cup of sea salt
Luke warm enema during the period of healing diet
Steam or hot tub bath or hot foot baths with epsom salt twice a week for 3 months. Try to apply olive oil before taking hot epsom salt bath
Sleep is one of the powerful lifestyle drugs which all of us need for prevention as well as healing any disease.
Repair and rejuvenation happen during rest:-
SLEEP DISORDER
For an adult, 7-8 hours of sleep is very important to keep the body active, let it heal, and restore its chemical balance.
SYMPTOMS OF SLEEP DISDORDERS
Anxiety
Weight gain
Lack of focus and concentration
Abnormal breathing patterns
Fatigue during daytime
Urge to sleep during the day
Unintentional wake or sleep schedule alteration
Experience abnormal movements while sleeping
Problems sleeping at least 3 nights per week for more than 3 months
Poor daytime functioning including:
Fatigue
Poor concentration
Impaired performance
Behavioral problems
Chronic pain
Headache
Nausea
COMMON TYPES OF SLEEP DISORDER
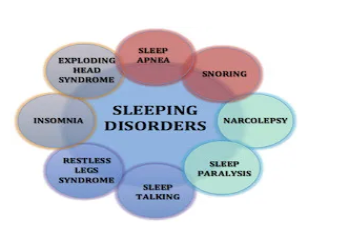
Chronic insomnia: You have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep most nights for at least three months and feel tired or irritable as a result.
Obstructive sleep apnea: You snore and have moments during sleep when you stop breathing that disrupt your sleep.
Sleep related movement disorder (SRMD) –
Restless legs syndrome: You have the urge to move your legs when you rest.
Narcolepsy: You can’t regulate when you fall asleep or how long you stay awake. During narcolepsy, a person feels sleep paralysis, a condition that makes it hard to move physically after waking up.
Shift work sleep disorder: You have trouble falling asleep and staying asleep and feel sleepiness at unwanted times due to your work schedule.
Delayed sleep phase syndrome: You fall asleep at least two hours after your desired bedtime and have difficulty waking up in time for school or work.
REM sleep Behavior disorder: It is the stage where most of the dream happens. During REM your brain activity looks very similar to brain activity while you’re awake
Parasomnias – In this type people show abnormal behaviours or movements during sleep. Some significant conditions with Parasomnias are sleepwalking, sleep talking, nightmares, bedwetting, jaw clenching or teeth grinding.
HANDLING SLEEP DISORDERS
Pranayama – Chandrabedi, Nadishodhan, Brahmari, 6-6-12 Breathing Technique, Yoganidra
Yogasanas like Shirsanana, Sarvangasana, Uttanasana, Viparitakarni, Paschimotanasana & Shavasana are helpful, Yoga Nidra and Shawasana are quite helpful when done during bedtime.
Avoid stimulators like Caffeine, alcohol, spicy food, tobacco etc. close to bedtime.
Heavy Meal close to bedtime can make one feel acidic and may cause difficulty falling asleep as metabolism of the body increases when digestive system is active.
Limit your screen time just before going to bed. Gadgets emit light which blocks melatonin
Keep room airy and darken the room 30 mins before bedtime so your brain gets signal it’s time for you to fall asleep now
Ensure a fixed bedtime routine for a sound sleep. It’s important to set our biological clock as per the routine
Hydrotherapy – Warm shower, warm foot bath, hot fomentation to the spine, cold hip bath with the feet in hot water before bedtime will drop your body temperature a bit which helps you sleep faster
Aim to meditate, visualize, and write affirmations 10-15 mins before bedtime
THE CURE
Pinch of nutmeg with water OR dash of nutmeg + tbsp of fennel + pinch of cinnamon – boil in water and consume 30 mins before bedtime
Food rich in amino acid tryptophan will release sleep hormone melatonin in the body – Pumpkin, Almonds, Organic A2 Milk, Yogurt etc. are good options for bedtime snacking.
Consuming chlorophyll rich food during daytime is more beneficial than consuming it during bedtime.
A warm cup of Chamomile/Lavender Tea helps to calm down the body and aids in better quality sleep.
Getting sun exposure & natural light during the day helps reset your body’s inner sleep clock
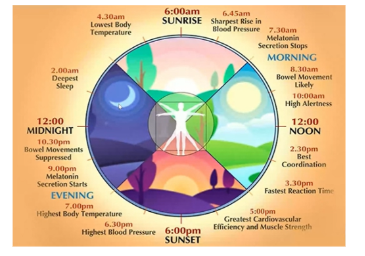
Follow circadian rhythm- Our body carries on its functions in tune wit a rhythm (4.00am to 12.00p.m-Body works on cleanup 12.00pm to 8.00pm – Body ready for digestion 8.00pm to 4.00pm – Assimilation)