WEIGHT MANAGMENT
Weight management is the habit of keeping body weight healthy with good eating, frequent exercise, and nutritious lifestyle choices. It is not just about losing unwanted weight but also about building up weight in a healthy fashion when necessary, so the body attains and maintains an optimal level overall. If you are underweight or even overweight, you can experience numerous health issues like hormonal imbalance, compromised immunity, lethargy, and elevation in chronic ailments. Healthy weight management means developing long-term habits like consuming nutrient foods in proper proportions, maintaining physical activity, having proper sleep, and stress management. This continuous process aids long-term health, decreases the risk of diseases of lifestyle, and enhances energy, mood, and general well-being.
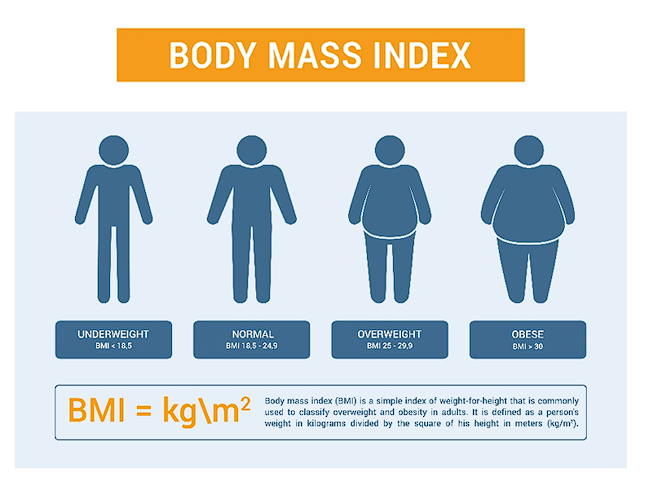
Here’s an example of BMI weight categories as per the World Health Organization (WHO):
Category | BMI Range | Health Risk |
Underweight | Less than 18.5 | Nutritional deficiencies, weakened immunity |
Normal weight | 18.5 – 24.9 | Lowest risk for weight-related diseases |
Overweight | 25 – 29.9 | Increased risk of chronic diseases |
Obesity (Class I) | 30 – 34.9 | High risk of heart disease, diabetes |
Obesity (Class II) | 35 – 39.9 | Very high risk of serious health issues |
Obesity (Class III / Severe) | 40 and above | Extremely high risk, life-threatening conditions |
If your body weight crosses a three-digit figure (100 kg and above), the risk of having a higher BMI and being in the obesity category is extremely high—particularly if your height is average or less than average. Excess weight in this group places a tremendous burden on your heart, joints, and metabolism, raising the risk of severe health issues like diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and joint diseases. A healthy weight maintained by proper eating, exercise, and lifestyle is necessary to avoid such complications as well as enhance overall health.
BMI (Body Mass Index) is calculated using a person’s weight and height with this formula:
BMI Formula: Weight (in kilograms)
BMI = —————————————-
Height ( in meters ) sq
Height influences BMI because the formula is weight divided by height squared.
If two individuals have the same weight but one is shorter, their BMI will be greater, so they can go into an overweight or obese class sooner than a person who is taller and of the same weight. In the same way, taller individuals require additional weight to achieve the same BMI as shorter individuals.
Reason of Weight Gain
- Overeating & High-Calorie Diet : Consumption of more calories than needed by the body—particularly fried, processed, and sweet foods—results in excess fat storage and weight gain over time.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sitting for long periods, no exercise, and a sedentary lifestyle decrease metabolism, making the body burn fewer calories.
- Hormonal Imbalance : Metabolism is disrupted and fat storage is encouraged by conditions such as thyroid issues, insulin resistance, or estrogen imbalance.
- PCOD / PCOS : Polycystic Ovarian Disease/Syndrome also involves hormones, tending to cause irregular periods, hunger, and weight gain, particularly around the waist.
- Stress & Emotional Eating : Stress releases cortisol into the body, which stimulates cravings for fatty and high-sugar foods and causes individuals to overeat with emotional ups and downs.
- Lack of Sleep : Inadequate sleep disrupts hunger hormones (ghrelin and leptin), leaving you hungrier, less energetic, and more prone to overeating.
- Medications : Some drugs such as steroids, antidepressants, and oral contraceptives tend to slow down metabolism or stimulate hunger, causing weight gain.
- Genetics & Family Inheritance : If family members are obese, it is easier to put on weight because of inherited metabolism and fat storage patterns.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle Habits : Missed meals, late-night meals, alcohol, cigarette smoking, and irregular lifestyles all help to add weight in the long run.
- Excessive Liquid Consumption
Drinking too many high-calorie liquids—such as sugary juices, sodas, milkshakes, and alcohol—adds hidden calories and leads to weight gain. - Steroid-Based Medications
Long-term use of steroids (for asthma, arthritis, etc.) often leads to fluid retention, increased appetite, and weight gain.
Common diseases associated with obesity

- Type 2 Diabetes – Having too much body fat, particularly around the middle, causes resistance to insulin, which makes it more difficult for the body to control blood sugar.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) – Excess weight puts more pressure on the heart and blood vessels, increasing blood pressure.
- Sleep Apnea – Fat cells in the neck and throat area can obstruct airways while sleeping, leading to pauses in breathing and poor quality of sleep.
- PCOD/PCOS – Obesity will exacerbate hormonal abnormalities in women, resulting in irregular menstrual cycles, cysts on the ovaries, and infertility.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux (GERD) – Excess fat in the abdomen puts stress on the stomach, forcing acid up into the esophagus.
- Osteoarthritis – Additional weight strains joints, particularly knees and hips, wearing away cartilage and causing pain.
- Heart Diseases – Elevated cholesterol, blood pressure, and inflammation due to obesity make heart attack and other cardiovascular issues more likely.
- Infertility – Changes in hormones associated with obesity may disrupt ovulation in females and semen quality in males.
- Some Cancers – Increased body fat is associated with cancers such as breast, colon, endometrial, and kidney cancer because of hormonal and inflammatory changes.
Common mistakes people make while trying to lose weight
- Skipping Meals
Others think skipping breakfast or lunch will save calories, but it usually does the opposite. The body shifts into “survival mode,” and metabolism slows down, and next thing you know, you will be overeating because of extreme hunger. Balanced meals eaten regularly work much better for sustained weight control.
- Crash Dieting
Crash diets cut calories drastically and may cause quick weight loss at first, but they are unsustainable. They often deprive the body of essential nutrients, leading to fatigue, hair fall, and weakness. Once the diet stops, people usually gain the lost weight back (yo-yo effect).
- Stopping After a Few Days
Most want overnight success and quit if they don’t notice changes after a week or two. True weight loss is a process—slow, consistent gains are better and more enduring than rapid solutions.
- Eating Too Much of “Healthy” Foods
Nuts, fruits, smoothies, and dry fruits are healthy foods that are calorie-dense. Consuming them in excess amounts can halt or even reverse weight loss. Portion control is important, even with healthy foods.
- Neglecting Exercise
Others pay attention to diet alone and ignore exercise. Exercise not only burns calories but also develops muscle, enhances metabolism, enhances mood, and keeps the body firm. Without exercise, weight loss is typically slower and less likely to last.
- Relying Only on Supplements
Weight-loss powders, fat-burning pills, or detox teas can promise miracles, but without diet and lifestyle adjustment, they seldom deliver. Supplements by themselves can actually be bad for your health in the long term as well.
- Not Sleeping Enough
Poor sleep stimulates hunger hormones (ghrelin) and suppresses satiety hormones (leptin) and thus makes you hungrier. Sleep deprivation also saps energy for exercise and makes it more difficult to resist cravings.
- Stress Eating
When under stress, most people seek comfort foods such as ice cream, chips, or chocolates. Stress boosts the cortisol hormone, which encourages fat storage around the stomach area. Stress management is critical in controlling weight.
- Setting Unrealistic Goals
Attempting to shed 10 kg in one month or anticipating rapid body changes creates frustration. Unrealistic goals encourage individuals to unhealthy means and lead to disappointment. Smaller, achievable goals maintain high motivation.
- Inconsistency
Being disciplined for a few days and then having long breaks, regular “cheat meals,” or unsystematic workouts hinder progress. Consistency is the most significant point for long-term weight loss outcomes.
TREATMENT

- Regular Exercise
30–45 minutes of walking, jogging, cycling, or weight training at least daily burns calories and boosts metabolism. Wheatgrass complements this by giving you energy and endurance so that you can exercise without exhaustion
- Yoga & Meditation
Yoga maintains flexibility of the body and serenity of the mind. Stress is one of the main causes of overeating, and wheatgrass mitigates stress by balancing the hormones and detoxifying the system, thus enhancing yoga sessions.
- Balanced Food Diet
Consume more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and proteins and less junk and sugar foods. Wheatgrass is full of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which decrease hunger pangs and make you feel fuller for longer.
- Sufficient Sleep & Rest
Imbalanced hormones and night cravings are caused by inadequate sleep. With its blood-sugar-controlling and cleansing properties, wheatgrass promotes quality sleep, allowing the body to recover and lose weight naturally.
- Herbs commonly blended with Wheatgrass Powder : Wheatgrass (Base Ingredient) , Ashwagandha , Giloy (Guduchi) , Triphala , Aloe Vera.
- Therapy: Full Body Massage , Steam Bath , Enema , Tub Bath.

Reasons for Underweight
- Fast Metabolism
Individuals with naturally rapid metabolism metabolize calories faster than normal, and it becomes hard to gain or hold weight despite eating frequently.
- Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency leads to anemia, which results in fatigue, weakness, and loss of appetite. This decreases food consumption and leads to underweight.
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 is necessary for energy production as well as red blood cell formation. Deficiency can result in tiredness, loss of appetite, and gastrointestinal symptoms, resulting in weight loss.
- Irregular Diet
Missing meals, missing meals at odd hours, or failing to take sufficient nutrient-containing foods bars the body from receiving calories and nutrients it requires, making it underweight.
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 1
In Type 1 diabetes, the body is unable to make insulin, and hence glucose is not absorbed by cells as it should be. This results in weight loss in spite of a good appetite.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders (GID)
Issues such as ulcers, IBS, celiac disease, or ongoing diarrhea hinder nutrient absorption, which makes it difficult for the body to achieve healthy weight.
- Depression
Mental disorders tend to decrease hunger, appetite, and energy levels, producing low calorie consumption and weight loss over time.
- Excessive Drinking of Alcohol
Alcohol suppresses hunger, disrupts the absorption of nutrients, and is harmful to the digestive system and liver, all of which result in being underweight.
Results of Being Underweight
- Fatigue & Low Energy : Inadequacy of calories makes the body week and lowers stamina Consume energy-enhancing foods such as dates, bananas, soaked dry fruits, and do pranayama for energy.
- Malnutrition : Inadequate consumption of protein and calories results in overall weakness. Solution: Include protein foods such as pulses, nuts, seeds, and natural food supplements such as wheatgrass or alfalfa.
- Fertility & Menstrual Issues : Underweight disrupts hormones and leads to irregular menstruation and infertility. Solution: Do yoga (Bhujangasana, Setu Bandhasana), consume sesame seeds, jaggery, and balanced food.
- Deficiencies of Nutrients : Iron, calcium, and vitamin deficiency causes anemia, poor bone health, and poor health. Consume leafy greens, whole grains, sprouts, and sunlight for Vitamin D.
- Frail Bones (Osteoporosis) :Underweight individuals are susceptible to fractures and weak bones. Solution: Include calcium foods (ragi, almonds, sesame seeds), sunlight, and weight-bearing exercise.
- Poor Wound Healing :Lack of protein postpones healing and repair of tissues. Solution: Consume sprouts, legumes, honey, and have aloe vera juice for quick recovery.
- Hair, Skin & Dental Problems : Deficiencies lead to hair loss, dryness of the skin, brittle nails, and weak teeth. Solution: Add coconut oil, flaxseeds, vitamin C fruits, and daily oil massage.
- Problems in Growth & Development : In children, underweight lags behind in physical and mental development. Solution: Provide them with balanced home-cooked food, milk, ghee, nuts, and adequate rest.
- Higher Risk of Surgery Complications : Slow post-surgery recovery from poor nutrient stores. Solution: Tonic up immunity for surgery with plant tonics such as chyawanprash, wheatgrass, and soups.
- Low Muscle Tone : Muscles get decomposed by the body for energy, and this results in frailty. Solution: Add resistance exercises, soaked almonds, milk, and pulses for natural protein.
- Liver Diseases : Poor diet compromises liver function and predisposes to disorders. Solution: Do not consume alcohol, include bitter foods such as neem, karela, and consume wheatgrass juice for liver health.
- Some Kinds of Cancer Malnutrition and deficiency over prolonged periods can increase the risk of cancer. Solution: Consume antioxidant foods such as amla, turmeric, green tea, and ensure high immunity.
TREATMENT

- Appropriate Fat-Rich Diet :Ghee, nuts, seeds, avocados, and coconut are healthy fats that support calorie consumption and weight gain.
- High Protein Diet :Muscle mass and strength rely on proteins. Eat sprouts, pulses, legumes, soya, dairy foods, and protein-rich natural supplements.
- Good Digestion is Needed : Despite the proper diet, incorrect digestion hinders weight gain. Yoga asanas, daily consumption of buttermilk, ginger, and ajwain, and proper digestion and nutrient assimilation enhance digestion and absorption of nutrients.
- Alfalfa Powder Support : Alfalfa powder contains high proteins, vitamins, and minerals. It stimulates appetite, corrects digestion, enhances nutrient uptake, and gives natural strength—making it very effective in treating underweight.
- Use Saffron4Health Alfalfa Powder, a synergistic combination of Ashwagandha, Alfalfa, Moringa, Shatavari, Kaunch, and Amla. This blend of herbs aids in enhancing appetite, energy levels, digestion, hormones, and delivering vital vitamins and minerals.
THERAPY
- Full Body Massage (Abhyanga): Enhances blood flow, increases appetite, calms the nervous system, and supports improved absorption of nutrients. Apply warm sesame or coconut oil for nutrition.
- Sun Bath (Heliotherapy) : Early morning sunlight exposure increases Vitamin D, increases bone strength, and enhances overall metabolism.
- Steam Bath : Assists in detoxification and enhances blood circulation, making the digestive system more efficient.
- Mud Therapy (with Saffron Natural Mud) : Using Saffron Natural Mud packs on the stomach enhances digestion and stimulates appetite, and mud packs on the eyes reduce stress and promote sleep. Whole body mud baths with Saffron Natural Mud detoxify, cool the body, and refresh the system.
- Enema Therapy : A cleansing enema with herbal decoctions eliminates toxins from the colon and aids in more efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients.
- Hydrotherapy (Tub Bath / Contrast Bath) : Alternating hot and cold baths stimulate metabolism, enhance circulation, and aid energy levels.
- Yoga & Pranayama : Asanas such as Bhujangasana, Vajrasana, and Setu Bandhasana facilitate digestion and strength. Pranayama such as Anulom Vilom and Bhramari decrease stress and regulate hunger-controlling hormones.
- Rest & Relaxation Therapies : Yoga Nidra and meditation decrease stress and enhance sleep, which are crucial for healthy weight gain.