What is infertility (part 2)
What is Infertility?
Infertility is a male or female reproductive system condition characterised by the inability to achieve pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Millions of people are affected by infertility, which has an impact on their families and communities. According to estimates, one in every six people of reproductive age worldwide will experience infertility at some point in their lives.
- HOW COMMON IS INFERTILITY:
Infertility affects both males and persons who were designated male at birth (AMAB) and women and people who were assigned female at birth (AFAB). Infertility is a very prevalent problem. In the United States, one in every five women between the ages of 15 and 49 suffers from primary infertility, while one in every twenty suffers from secondary infertility. Infertility affects around 48 million couples worldwide.
What is the main cause of infertility?

Fertility is frequently caused by ovulation issues (the monthly release of an egg from the ovaries). Some issues prohibit eggs from being released at all, while others prevent eggs from being released during some cycles but not others.
FEMALE INFERTILITY
What is FEMALE infertility?
Infertility is an illness that impairs or limits a person’s capacity to become pregnant and give birth to a child. This is usually identified after one year of attempting to get pregnant for heterosexual couples.

One-third of the causes of infertility in heterosexual couples are due to a male problem, one-third to a female problem, and one-third to a combination of unknown causes. When the female spouse is proven to be the source of infertility, it is referred to as female infertility or “female factor” infertility.
\How common is female infertility?
Infertility is a common disease. At least 10% of women deal with infertility of some kind. The chances of being infertile increase as a woman ages.
What causes female infertility?
There are many possible causes of infertility. However, it can be difficult to pinpoint the exact cause, and some couples have “unexplained” infertility or “multifactorial” infertility (multiple causes, often both male and female factors). Some possible causes of female factor infertility can include:
roblems with the uterus: This includes polyps, fibroids, septum or adhesions inside the cavity of the uterus. Polyps and fibroids can form on their own at any time, whereas other abnormalities (like a septum) are present at birth. Adhesions can form after surgery like a dilation and curettage
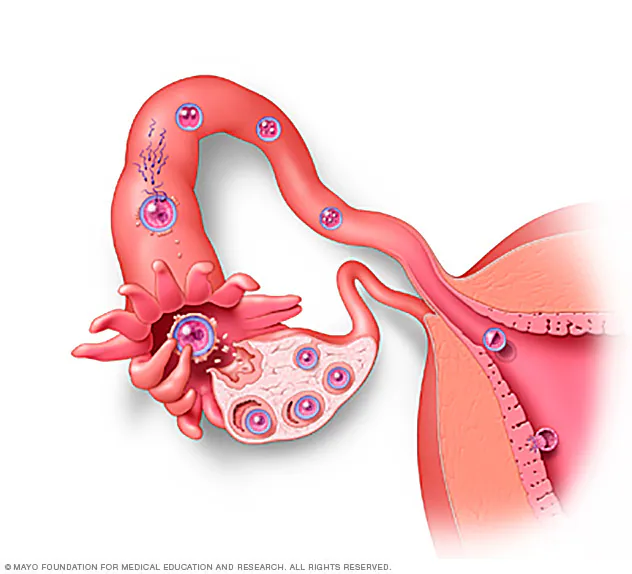
- Problems with the fallopian tubes: The most common cause of “tubal factor” infertility is pelvic inflammatory disease, usually caused by chlamydia and gonorrhoea.
- Problems with ovulation: There are many reasons why a woman may not ovulate (release an egg) regularly. Hormonal imbalances,

a past eating disorder, substance abuse, thyroid conditions, severe stress and pituitary tumours are all examples of things that can affect ovulation.

- Problems with egg number and quality: Women are born with all the eggs they will ever have, and this supply can “run out” early before menopause.
In addition, some eggs will have the wrong number of chromosomes and cannot fertilize or grow into a healthy fetus. Some of these chromosomal issues (such as “balanced translocation”) may affect all of the eggs. Others are random but become more common as a woman gets older.
What effect does ageing have on female infertility?
A woman’s chances of becoming pregnant decrease as she aged. Because many couples wait until their 30s or 40s to have children, age is becoming a more common factor in female infertility. Women over the age of 35 are more likely to experience fertility problems. The following are some of the reasons for this:
- The total number of eggs is decreasing.
- More eggs have an unusually large number of chromosomes.
- A higher risk of developing other health problems.

How is female infertility treated?
Once your healthcare provider has diagnosed female infertility and pinpointed the cause, there are a variety of treatment options. The cause of infertility guides the type of treatment. For example, structural problems may be treated through surgery, while hormonal medications can be used for other issues (ovulation issues, thyroid conditions).
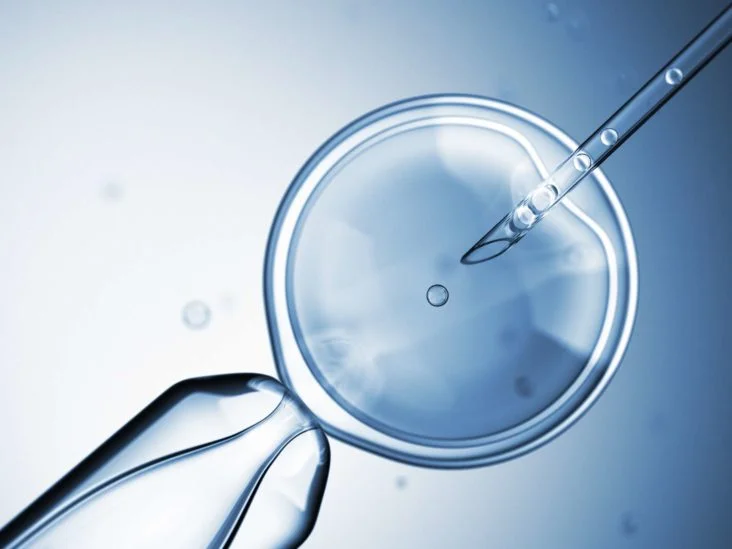
Many patients will require artificial insemination (injecting washed sperm into the uterus after ovulation) or in vitro fertilization (fertilizing eggs with sperm in the lab to make embryos, then transferring the embryo into the uterus).
Adoption and gestational surrogacy may also be options for women with infertility who wish to start a family.
Reasons for female infertility:-
Many factors can increase a woman’s risk of female infertility. General health conditions, genetic (inherited) traits, lifestyle choices and age can all contribute to female infertility. Specific factors can include:
- Age.
- Hormone issue that prevents ovulation.
- Abnormal menstrual cycle.
- Obesity.
- Being underweight.

- Having a low body-fat content from extreme exercise.
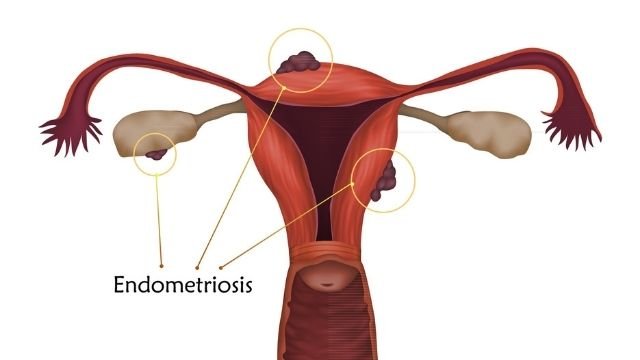
- Endometriosis.
- Structural problems
- Uterine fibroids.

- Primary Ovary Insufficiency.
- Excessive substance use (heavy drinking).
- Smoking.
- A past ectopic pregnancy.