Women’s Health and Naturopathy
Women’s Health and Naturopathy

Women’s health is a complex and multifaceted aspect of healthcare that requires a holistic approach. Naturopathy, with its focus on natural remedies and lifestyle changes, offers a unique perspective on maintaining and improving women’s health. In this article, we will explore various aspects of women’s health and how naturopathy can play a significant role in promoting wellness.
Women’s health encompasses a range of issues that are unique to women, including reproductive health, hormonal balance, and mental health. Factors such as menstrual cycles, pregnancy, menopause, and the female anatomy require specialized care and attention.
This article explores the intersection of women’s health and naturopathy, focusing on holistic approaches to well-being. It begins with an introduction to the topic, highlighting the importance of a holistic approach. Understanding the female body’s physiology and hormonal balance is crucial, as discussed in the second section.
The article then delves into common women’s health concerns and how naturopathy offers unique approaches to address them. Nutrition and diet play a significant role in women’s well-being, and naturopathic principles guide dietary recommendations.
Herbal medicine and botanical remedies are key components of naturopathy, particularly for women’s health. Mind-body practices, including stress management techniques, are highlighted for hormonal balance and overall wellness.
Naturopathic therapies for menstrual health and menopause are discussed, emphasizing natural approaches to support these phases of life. Integrative approaches to fertility and reproductive health are also explored, showcasing the holistic nature of naturopathic care.
Supporting women’s mental health naturally is a critical aspect, with lifestyle modifications playing a key role. The article concludes with a focus on empowering women through holistic healthcare practices, highlighting case studies and success stories in women’s health and naturopathy.
Introduction to Women’s Health and Naturopathy:
Women’s health is a multifaceted field that addresses the unique physiological, psychological, and emotional aspects of women’s well-being. It encompasses a range of issues, including reproductive health, hormonal balance, and mental wellness, that require a holistic approach to care.
Naturopathy, a form of alternative medicine, offers a holistic approach to healthcare that emphasizes natural remedies and lifestyle modifications. It recognizes the interconnectedness of mind, body, and spirit, viewing them as integral parts of overall health. Naturopathy aims to empower women by providing them with the knowledge and tools to take charge of their health and well-being.
One of the key principles of naturopathy is the belief in the body’s innate ability to heal itself when given the right support. This approach contrasts with conventional medicine, which often focuses on treating symptoms rather than addressing the underlying causes of health issues.
Naturopathic treatments for women’s health issues may include dietary changes, herbal medicine, physical therapies, and counseling. These treatments are aimed at restoring balance to the body and promoting overall health and wellness.
Women’s health is a complex and nuanced field that requires a holistic approach to care. Naturopathy offers a unique perspective on women’s health, emphasizing natural remedies and lifestyle changes to promote healing and empower women in taking control of their health.
Naturopathy, as a holistic approach to healthcare, focuses on individualized treatment plans, education, and preventive strategies to address the root causes of health issues and promote long-term wellness. This overview explores how naturopathic principles can be applied to women’s health, emphasizing key aspects such as hormonal balance, nutrition, herbal medicine, and lifestyle modifications.
One of the core principles of naturopathy is the recognition of the interconnectedness of the body, mind, and spirit in achieving optimal health. By understanding and addressing the underlying causes of health issues, rather than just treating symptoms, naturopathic practitioners aim to support the body’s natural healing abilities.
Hormonal balance is crucial for women’s health, as imbalances can lead to a range of issues such as menstrual irregularities, mood swings, and reproductive problems. Naturopathic treatments focus on restoring hormonal equilibrium through natural remedies and lifestyle changes.
Nutrition plays a vital role in women’s health, and naturopathy emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet rich in nutrients. Herbal medicine is another key component of naturopathic care, with a focus on using plant-based remedies to support the body’s healing processes.
Mind-body practices, such as yoga, meditation, and stress management techniques, are also integral to naturopathic care. These practices help women reduce stress, improve mental health, and enhance overall well-being.
Naturopathy offers a comprehensive and integrative approach to women’s health, addressing the root causes of health issues and promoting long-term wellness. By understanding the importance of hormonal balance, adopting a balanced diet, incorporating herbal remedies, and embracing mind-body practices, women can enhance their overall health and vitality.
Understanding the Female Body: Physiology and Hormonal Balance
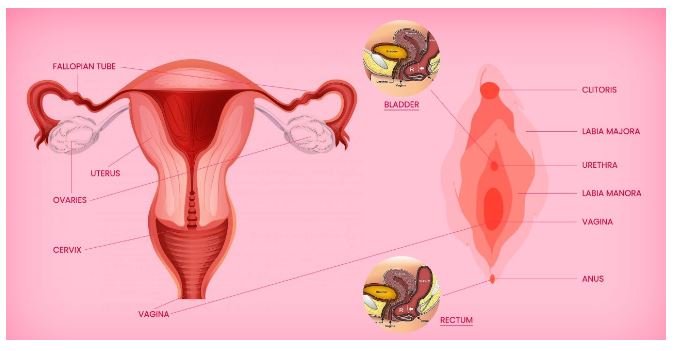
The female reproductive system is a complex and intricately designed network of organs and hormones that play a vital role in reproduction and overall health. In this article, we will explore the anatomy and function of the female reproductive organs, shedding light on the importance of hormonal balance in women’s health.
Primary Sex Organs: Ovaries
The ovaries are a pair of small, almond-shaped organs located in the lower abdomen. Their primary function is to produce eggs, or ova, which are necessary for reproduction. In addition to producing eggs, the ovaries also secrete female sex hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, which play a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle and supporting pregnancy.
Accessory Sex Organs
The female reproductive system also includes a system of genital ducts and external genitalia, which are collectively referred to as accessory sex organs.
Genital Ducts:
Fallopian Tubes: Also known as oviducts, the fallopian tubes are a pair of narrow tubes that extend from the ovaries to the uterus. They serve as the site of fertilization, where sperm meet and fertilize the egg.
Uterus: The uterus, or womb, is a pear-shaped organ located in the pelvis. Its main function is to house and nourish a developing fetus during pregnancy.
Cervix: The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It acts as a passageway for sperm to enter the uterus and for menstrual blood to exit the body.
Vagina: The vagina is a muscular canal that extends from the cervix to the external genitalia. It serves as the birth canal during childbirth and also functions as the outlet for menstrual blood.
External Genitalia:
Labia Majora: The labia majora are the outer folds of skin that surround the vaginal opening. They help protect the internal reproductive organs.
Labia Minora: The labia minora are the inner folds of skin located within the labia majora. They also help protect the vaginal opening.
Clitoris: The clitoris is a small, sensitive organ located at the top of the vulva, between the labia minora. It is highly sensitive to sexual stimulation and plays a role in sexual pleasure.
Female Reproductive Functions:
The female reproductive functions can be broadly divided into two major phases:
Preparation of the female body for conception and pregnancy, which involves the production and release of eggs, hormonal regulation, and preparation of the uterus for implantation.
The period of pregnancy itself, which involves the implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus, the development of the fetus, and the eventual birth of the baby.
The female reproductive system is a complex and intricate system that is essential for reproduction and the continuation of the human species. Understanding the anatomy and function of the primary and accessory sex organs is crucial for maintaining women’s reproductive health and overall well-being.
Physiological Anatomy of the Female Sexual Organs
The female reproductive system is a complex and fascinating network of organs and structures that work together to support the process of reproduction. Understanding the physiological anatomy of these organs is crucial for understanding how reproduction occurs in women.
The Female Reproductive Tract:
The human female reproductive tract consists of several key organs, including the ovaries, fallopian tubes (also known as uterine tubes), uterus, and vagina. Each of these organs plays a vital role in the process of reproduction.
- Ovaries: The ovaries are the primary female reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs, or ova. They also secrete female sex hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and support pregnancy.
- Fallopian Tubes: The fallopian tubes are narrow tubes that extend from the ovaries to the uterus. They serve as the pathway for eggs to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. Fertilization of the egg by sperm usually occurs in the fallopian tubes.
- Uterus: The uterus, also known as the womb, is a pear-shaped organ where a fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus during pregnancy. The walls of the uterus are lined with a thick layer of tissue called the endometrium, which thickens and sheds during the menstrual cycle.
- Vagina: The vagina is a muscular canal that extends from the cervix to the external genitalia. It serves as a passageway for menstrual blood to leave the body and also acts as the birth canal during childbirth.
Reproduction Process:
Reproduction in women begins with the development of eggs in the ovaries. Each month, during the middle of the menstrual cycle, a single egg is released from one of the ovaries in a process called ovulation. If the egg is fertilized by sperm, it travels through the fallopian tube to the uterus, where it implants in the uterine lining. The fertilized egg then develops into a fetus, placenta, and fetal membranes, eventually leading to the birth of a baby.
The female reproductive system is a remarkable and complex system that is essential for reproduction. The ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina all play crucial roles in this process, highlighting the intricate design of the female body.
Maintaining Hormonal Balance in Women:
Hormonal balance is crucial for women’s health and well-being, as fluctuations can lead to various symptoms, including mood swings. Understanding the hormonal regulation process can shed light on how these fluctuations occur and their impact on women’s health.
The Role of the Hypothalamus:
The hypothalamus, a part of the central nervous system located in the brain, plays a key role in regulating hormonal balance. It produces a hormone called Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to release further hormones.
Hormones Released by the Pituitary Gland:
The pituitary gland, often called the “master gland,” secretes several hormones, including:
- FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone): FSH plays a crucial role in ovarian changes, particularly in the development of follicles in the ovaries.
- LH (Luteinizing Hormone) – Female: LH is essential for ovulation, the process in which a mature egg is released from the ovary.
- LH – Male: In males, LH stimulates the production of testosterone, which is essential for sperm production.
- Prolactin: Prolactin is responsible for stimulating milk production (lactation) in the mammary glands.

The Menstrual Cycle and Hormonal Fluctuations:
In women, hormonal fluctuations occur throughout the menstrual cycle, which typically lasts about 28 days. The cycle can be divided into several phases:
- Menstrual Phase: This phase starts on the first day of menstruation and lasts about 5-7 days. During this phase, FSH levels rise, stimulating the ovaries to produce estrogen.
- Follicular Phase: This phase follows menstruation and lasts about 7-10 days. Estrogen levels continue to rise, stimulating the thickening of the uterine lining (endometrium).
- Ovulation: Occurring around day 14 of the cycle, ovulation is triggered by a surge in LH, leading to the release of a mature egg from the ovary.
- Luteal Phase: After ovulation, the ruptured follicle transforms into a structure called the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. Progesterone helps prepare the uterus for implantation of a fertilized egg.
- Menstruation: If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum breaks down, leading to a drop in estrogen and progesterone levels. This drop triggers menstruation, and the cycle begins again.
Maintaining hormonal balance is essential for women’s health and well-being. Understanding the complex interplay of hormones in the menstrual cycle can help women better manage their hormonal health and address any issues that may arise. By being aware of their bodies and seeking appropriate medical advice, women can ensure that their hormones remain balanced, supporting overall health and vitality.
Common Women’s Health Concerns and Naturopathic Approaches:

Naturopathy offers natural remedies and holistic approaches to common women’s health concerns. These include menstrual irregularities, hormonal imbalances, menopausal symptoms, reproductive health issues, mental health, and chronic conditions. Naturopathic treatments focus on dietary changes, herbal remedies, lifestyle modifications, and stress management techniques to address these concerns and promote overall well-being. Working with a qualified naturopathic doctor can help women tailor a personalized treatment plan to meet their specific needs.
Most Common Female Health Issues:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by the overproduction of androgens, which are male sex hormones that are typically present in small amounts in women. The name “polycystic ovary syndrome” refers to the numerous small cysts, or fluid-filled sacs, that form in the ovaries.

Symptoms of PCOS:
PCOS can present with a variety of symptoms, which can vary in severity among individuals. Some common symptoms include:
- Missed or irregular periods, or very light periods
- Enlarged ovaries or ovaries with many cysts
- Excess hair growth on the face, chest, stomach, or back (hirsutism)
- Weight gain, particularly around the abdomen
- Acne or oily skin
- Male-pattern baldness or thinning hair
- Infertility
- Skin tags, which are small pieces of excess skin that may appear on the neck or armpits
- Dark or thick skin patches on the back of the neck, in the armpits, or under the breasts
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact cause of PCOS is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Insulin resistance, in which the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, is also thought to play a role in the development of PCOS. Other risk factors for PCOS include obesity, a family history of the condition, and being of certain ethnicities, such as South Asian or Hispanic descent.
Treatment and Management:
Treatment for PCOS focuses on managing symptoms and reducing the risk of complications. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise, are often recommended as first-line treatment. Medications may also be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and improve insulin sensitivity. In some cases, fertility treatments may be necessary for women trying to conceive.
PCOS is a common hormonal disorder that can have a significant impact on women’s health and well-being. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for PCOS, women can take proactive steps to manage the condition and improve their quality of life. Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare providers are essential for women with PCOS to ensure that they receive appropriate care and support.
2. Dysmenorrhea: Causes and Naturopathic Approaches: Dysmenorrhea, commonly known as painful menstruation, is a prevalent issue among women. It is often linked to an unhealthy lifestyle, including poor diet and high stress levels, leading to a weakened state of the body and particularly the reproductive organs. Naturopathy offers holistic approaches to manage dysmenorrhea, focusing on diet and hydrotherapy.

Symptoms and Types: Dysmenorrhea can manifest as pain before or during menstruation. There are two main types:
- Primary Dysmenorrhea: This occurs when women experience pain for 4-5 hours at the onset of menstruation.
- Secondary Dysmenorrhea: This is characterized by pain that begins before menstruation or when menstruation fails to start. Secondary dysmenorrhea is considered more severe than primary dysmenorrhea.
Naturopathic Protocol: Naturopathic treatments for dysmenorrhea include dietary adjustments and hydrotherapy techniques. Hot hip baths just before menstruation and cold hip baths between periods can be beneficial. Here is a basic protocol:
- Hot Hip Bath: Duration of 8-10 minutes at a water temperature of 100°F, gradually increasing to 120°F.
- Cold Hip Bath: Duration of 10-15 minutes at a water temperature of 50°F to 65°F.
Dietary Recommendations: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help alleviate symptoms of dysmenorrhea. Avoiding processed foods, caffeine, and alcohol is also advised.
Dysmenorrhea is a common issue that can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life. By adopting naturopathic approaches such as dietary modifications and hydrotherapy, women can manage the symptoms of dysmenorrhea and improve their overall well-being. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare practitioner before starting any new treatment regimen.
3. Menorrhagia or excessive Menstruation: Menorrhagia, or excessive menstrual bleeding, is a common issue among women and is often indicative of an underlying blood deficiency, particularly in calcium. Naturopathy offers holistic approaches to manage menorrhagia, focusing on rest, diet, and cleansing the body of toxins.
Causes and Symptoms:
Menorrhagia can be caused by various factors, but a toxic condition of the body is often the root cause. Symptoms include profuse menstrual flow, fatigue, and weakness.
Naturopathic Protocol: Naturopathic treatments for menorrhagia focus on dietary modifications and lifestyle changes. Here is a basic protocol:
- Rest and Bed Rest: Patient should be confined to bed with the bottom raised four to five inches to aid in blood circulation.
- Avoid Stimulants: Stimulants should be avoided, as they can increase blood flow.
- No Over-Exercising: After the bleeding has stopped, the patient should avoid over-exercising or straining the body in any way.
- Natural Diet: Adopting a full natural diet with fresh raw vegetable salads twice daily is recommended. This helps replenish essential nutrients.
- All-Fruit Diet: Starting with an all-fruit diet for about five days can help cleanse the system. This includes fresh, juicy fruits like apples, pears, grapes, grapefruits, oranges, pineapples, peaches, and melons. No other food should be consumed during this period.
Managing menorrhagia, or excessive menstrual bleeding, requires a holistic approach that addresses the underlying causes and promotes overall health and well-being. Naturopathy offers a comprehensive treatment plan that includes dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and specific therapies to help alleviate symptoms and restore balance to the body.
Dietary Recommendations:
- All-Fruit Diet: Starting with an all-fruit diet for two or three consecutive days at monthly intervals can help cleanse the system.
- Balanced Diet: After the all-fruit diet, adopting a well-balanced diet consisting of seeds, nuts, grains, vegetables, and fruits is crucial. Emphasis should be on iron-rich foods like apricots, milk, eggs, and nuts.
- Raw Juices: Raw juices such as spinach, red beet, and grape juice are beneficial for menstrual disorders.
- Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 supplements can help restore a normal menstrual cycle.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Dry Friction: Dry friction, using a cotton cloth or any other normal cloth, should be done regularly in the morning.
- Cold Hip Baths: Cold hip baths should be taken regularly, except during the menstrual period.
- Exercise: Outdoor exercise and deep breathing exercises are important and should be practiced daily.
Other Recommendations:
- Cleanliness: Scrupulous cleanliness is essential for successful treatment.
- Avoidance of Certain Foods: Avoiding white flour products, sugar, confectionery, cakes, pastries, sweets, refined cereals, flesh foods, tinned or preserved foods, strong tea, coffee, pickles, condiments, and sauces is advised.
- Avoidance of Smoking: Smoking should be completely avoided, as it can aggravate menstrual disorders.
Naturopathic management of menorrhagia focuses on restoring balance to the body through dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and specific therapies. By following a holistic approach, women can effectively manage menorrhagia and improve their overall health and well-being. It is important to consult with a qualified naturopathic doctor to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets individual needs.
4. Leucorrhea: Leucorrhea, commonly known as whites, is characterized by a whitish discharge from the female genitals. It is considered an abnormal condition of the reproductive organs and, if left untreated, can become chronic. Naturopathy offers holistic approaches to manage leucorrhea, focusing on diet, lifestyle, and specific therapies.

Causes and Symptoms:
Leucorrhea is often associated with a toxic or imbalanced state of the body. Symptoms may include weakness, tiredness, lumbar pain, calf pain, abdominal dragging sensation, constipation, frequent headaches, intense itching, irritability, and black patches under the eyes.
Naturopathic Protocol:
Naturopathic treatments for leucorrhea focus on dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and specific therapies to eliminate toxins and restore balance to the body. Here is a basic protocol:
- Fasting: Fasting for three or four days with lemon water or fruit juices can help eliminate morbid matter from the body.
- All-Fruit Diet: After fasting, adopting an all-fruit diet for about a week can be beneficial. This includes fresh, juicy fruits such as apples, pears, grapes, grapefruits, oranges, pineapples, and peaches.
- Diet for Anemia: If the patient is anemic or underweight, the diet may include fruits and milk.
- Avoidance of Certain Foods: Avoiding white flour products, white sugar, fried and greasy foods, condiments, preserves, tea, and coffee is advised.
- Treatment through Water: Cold hip baths twice a day for 10 minutes can help relieve congestion in the pelvic region. A warm vaginal douche at 30° to 40°C can aid in general cleaning and elimination of the discharge.
Leucorrhea can be effectively managed with a holistic approach that addresses the underlying causes and promotes overall health and well-being. Consulting with a qualified naturopathic doctor is important to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Managing Menstrual Disorders: A Holistic Diet Approach
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing menstrual disorders and promoting overall health. Naturopathy recommends specific dietary guidelines to help alleviate symptoms and restore balance to the body.
Dietary Recommendations:
- Upon Arising: Start your day with a glass of lukewarm water mixed with freshly-squeezed lime juice and honey. This helps kickstart your metabolism and aids digestion.
- Breakfast: Include fresh fruits and a glass of milk in your breakfast. Fruits are rich in vitamins and minerals, while milk provides essential nutrients like calcium and protein.
- Lunch: Opt for a bowl of freshly-prepared steamed vegetables, whole wheat chapatis, and a glass of buttermilk. This provides a balanced mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fiber.
- Mid-Afternoon: Have a glass of fruit juice or vegetable juice to keep you hydrated and provide additional nutrients.
- Dinner: Enjoy a bowl of fresh green vegetable salad and mung bean sprouts with lime juice dressing. This light and nutritious meal aids digestion and provides essential vitamins and minerals.
- Bedtime: Before bed, have a glass of fresh milk or an apple. Milk helps in inducing sleep and provides calcium, while apples are rich in fiber and antioxidants.
- Avoid Certain Foods: Avoid white flour products, sugar, confectionery, cakes, pastries, sweets, refined cereals, flesh foods, heavy or greasy foods, tinned or preserved foods, strong tea, coffee, pickles, condiments, and sauces. Smoking should also be completely avoided, as it can aggravate menstrual disorders.
- Lifestyle Recommendations: Care for your body with scrupulous cleanliness. Fresh air, outdoor exercise, and deep breathing are also important and should be practiced daily to promote overall health and well-being.
A well-balanced diet combined with healthy lifestyle practices can help manage menstrual disorders effectively. It is important to consult with a healthcare practitioner or naturopath to develop a personalized diet plan that meets your individual needs.
Additional Measures for Managing Menstrual Disorders
In addition to dietary changes, certain lifestyle modifications and therapies can further support the management of menstrual disorders. These measures aim to alleviate symptoms, promote hormonal balance, and improve overall well-being.
Dietary Recommendations:
- Short Periods on All-Fruit Diet: Spending two or three days on an all-fruit diet at monthly intervals can help cleanse the system and maintain overall health.
- Frequent Small Meals: Instead of three large meals, opt for six small meals throughout the day. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevents overeating.
Avoidance of Certain Foods:
- Meats: Reducing or eliminating meat consumption can help reduce inflammation and improve hormonal balance.
- Sugar and White Flour: These should be avoided as they can exacerbate hormonal imbalances and inflammation.
- Tea, Coffee, and Soft Drinks: These beverages can disrupt hormonal balance and should be limited or avoided.
- Fried Foods and Candies: These can contribute to inflammation and should be avoided.
- Condiments and Pickles: These can be high in sodium and may exacerbate bloating and water retention.
Other Measures:
- Cold Hip Bath: Taking a cold hip bath for 10 minutes daily can help relieve congestion in the pelvic region. However, this should be suspended during the menstrual period.
- Fresh Air and Moderate Exercise: Spending time outdoors and engaging in moderate exercise can help improve circulation, reduce stress, and support overall health.
Incorporating these additional measures, along with dietary changes, can help manage menstrual disorders effectively. It is important to consult with a healthcare practitioner or naturopath to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets your individual needs.
Herbal Remedies for Women’s Health: A Traditional Approach

Indian traditional medicine, including Ayurveda, offers a rich array of herbal remedies to support women’s health. These herbs have been used for centuries and are known for their rejuvenating and therapeutic properties. Here are some commonly used herbs with their Indian names and benefits:
- Ashoka (Saraca indica): This herb is known for its ability to regulate the menstrual cycle and manage menstrual disorders such as excessive bleeding and pain.
- Shatavari (Asparagus racemosus): Shatavari is renowned for its rejuvenating properties and is particularly beneficial for female reproductive health, especially during menopause.
- Kumari (Aloe Vera): Aloe Vera is not only beneficial for skin and digestion but also helps in managing menstrual disorders and promoting overall well-being.
- Triphala: Triphala is a combination of three fruits—amla, haritaki, and bibhitaki—that supports digestive health, which is crucial for women’s overall health.
- Lodhra (Symplocos racemosa): Lodhra is used in Ayurveda to support reproductive health and manage menstrual disorders.
- Manjistha (Rubia cordifolia): This herb helps maintain hormonal balance and promotes healthy blood circulation, which is essential for women’s health.
- Gokshura (Tribulus terrestris): Gokshura supports urinary and reproductive health, particularly in women with urinary tract issues.
- Dashamoola: A blend of ten roots, Dashamoola supports female reproductive health and helps alleviate menstrual discomfort.
- Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa): Punarnava is known for its diuretic properties and helps manage water retention, which is common during menstruation and menopause.
- Rasna (Pluchea lanceolata): Rasna is used to relieve menstrual cramps and muscle spasms, promoting comfort during menstruation.
These herbal remedies offer a natural and holistic approach to women’s health, addressing various issues such as menstrual disorders, hormonal balance, and reproductive health. However, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare practitioner before incorporating these herbs into your routine, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, or have any underlying health conditions.
In conclusion, traditional Indian herbal remedies offer a natural and holistic approach to supporting women’s health. These herbs, with their rejuvenating and therapeutic properties, have been used for centuries to manage menstrual disorders, promote hormonal balance, and support overall well-being.
However, it is crucial to approach herbal remedies with caution and consult with a qualified healthcare practitioner before incorporating them into your routine. This is especially important if you are pregnant, nursing, or have any underlying health conditions.
By combining traditional wisdom with modern healthcare practices, women can harness the benefits of these herbal remedies to enhance their health and well-being.